Figure 3.
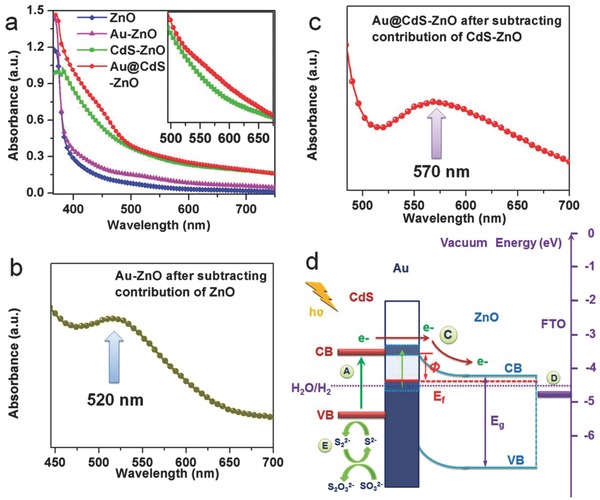
a) Optical absorption spectra of photoelectrodes. The inset is enlarged spectra of CdS‐ZnO and Au@CdS‐ZnO. b) Optical absorption spectrum of Au‐ZnO photoelectrode after subtracting contribution of ZnO. c) Optical absorption spectrum of Au@CdS‐ZnO photoelectrode after subtracting contribution of CdS‐ZnO. d) Electron transfer path of Au@CdS‐ZnO. Process A: photon absorption and electron excitation of CdS shell; B: plasmon resonance of Au core; C: energetic electron transfer from CB of CdS shell over the potential energy barrier of Au into ZnO; D: electron conduction as a majority carrier within the ZnO to the FTO glass; E: reduction of the photogenerated holes. Φ for the Schottky barrier, E f for the Fermi energy, E g for the ZnO bandgap, and CB and VB for conduction band and valence band, respectively.
