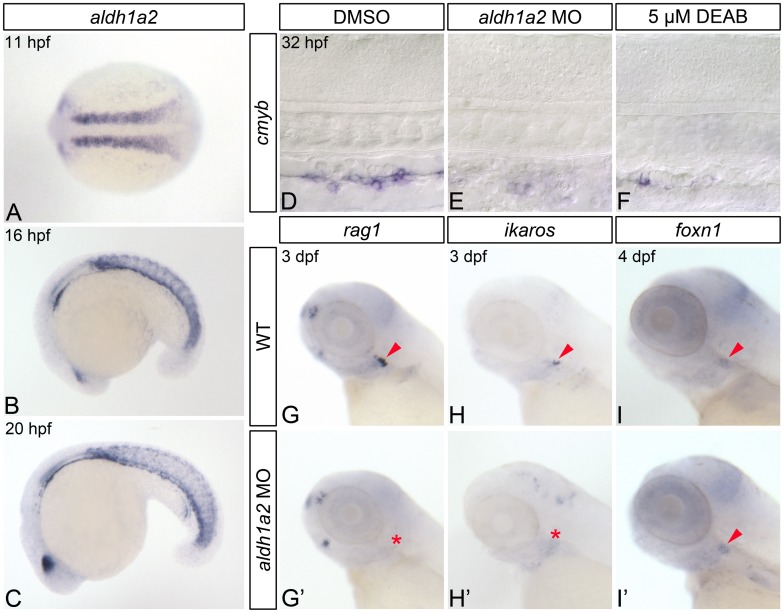
Fig 1. RA-deficient embryos demonstrate impaired HSC formation.
(A-C) In situ hybridization analyses of aldh1a2 gene expression in wild type (WT) embryos. (A) Expression within the somites at 11 hpf, shown in dorsal view with anterior to the left. Somitic expression persists in 16 hpf (B) and 20 hpf (C) embryos, shown in lateral view with anterior to the left. (D-F) Representative flat-mounted embryos following in situ hybridization analysis of cmyb gene expression at 32 hpf. Lateral view of gene expression in the dorsal aorta region of the trunk is shown with anterior to the left. Compared to DMSO-treated controls (D) aldh1a2-morphants (E), and 5 μM DEAB-treated embryos (F) exhibit nearly abolished cmyb expression. (G-H’) In situ hybridization analyses of common lymphoid progenitor gene expression in 3 dpf embryos. Lateral view of gene expression in the head is shown with anterior to the left. Arrowheads and asterisks indicate thymus. Compared to WT embryos (G, H), aldh1a2-morphants exhibit nearly abolished thymic rag1 (G’) and ikaros (H’) expression. (I, I’) Representative embryos following in situ hybridization analysis of foxn1 thymic epithelial cell gene expression in 4 dpf embryos. Lateral view of gene expression in the head is shown with anterior to the left. Arrowheads indicate thymus. WT embryos (I) and aldh1a2-morphants (I’) exhibit similar thymic foxn1 expression levels.