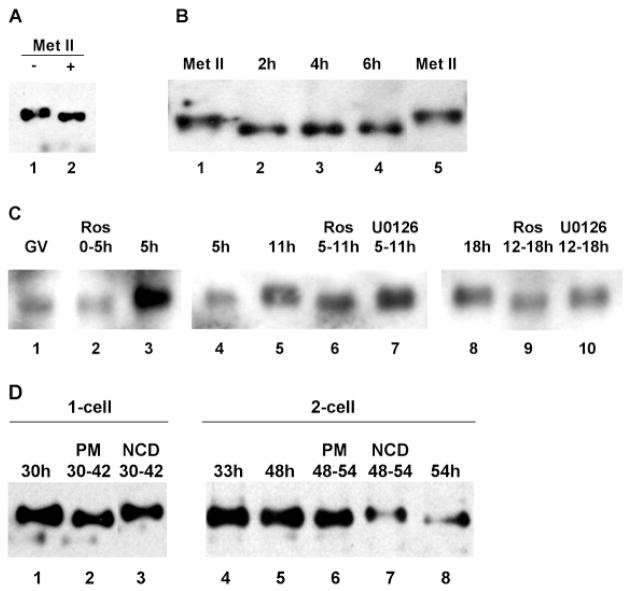
Fig. 6.
Control of SLBP phosphorylation. (A) Extracts from 20 metaphase II oocytes were incubated without (lane 1) or with phosphatase treatment (lane 2) and immunoblotted using the anti-SLBP antiserum. (B) Dephosphorylation of SLBP following oocyte activation. Unfertilized eggs were parthenogenetically activated and samples were collected at the indicated times after activation and analyzed by immunoblotting using the anti-SLBP antiserum (lanes 2–4). Lanes 1 and 5 are oocytes arrested at metaphase II; 25 eggs per lane. (C) Control by cyclin-dependent kinase of SLBP phosphorylation. (Lanes 1–3) GV-stage oocytes were collected; one sample was harvested immediately (lane 1, 80 oocytes) and the others were incubated for 5 hours in the presence (lane 2, 75 oocytes) or absence (lane 3, 67 oocytes) of roscovitine. (Lanes 4–7) GV-stage oocytes were collected and incubated for 5 hours. Those that underwent GVBD were either harvested immediately (lane 4) or at 11 hours (lane 5) or treated for the indicated period with roscovitine (lane 6) or U0126 (lane 7); 25 oocytes per lane. (Lanes 8–10) GV-stage oocytes were collected and incubated for 12 hours. Those that produced a polar body were incubated for an additional 6 hours in control medium (lane 8) or in the presence of roscovitine (lane 9) or U0126 (lane 10); 25 oocytes per lane. All samples were immunoblotted using the anti-SLBP antiserum. The films showing lanes 1–3, 4-7, and 8–10 were not exposed for the same lengths of time. (D) Phosphorylation of SLBP at mitotic M-phase. Embryos at the 1- or 2-cell stage were collected at the indicated times (hours post-hCG). Puromycin (PM, lanes 2 and 6) or nocodazole (NCD, lanes 3 and 7) treatment was performed for the period indicated, after which embryos were collected for immunoblotting using the anti-SLBP antiserum. All control embryos had cleaved by the end of the treatment period, whereas none of the drug-treated embryos had done so; 25 eggs per lane.