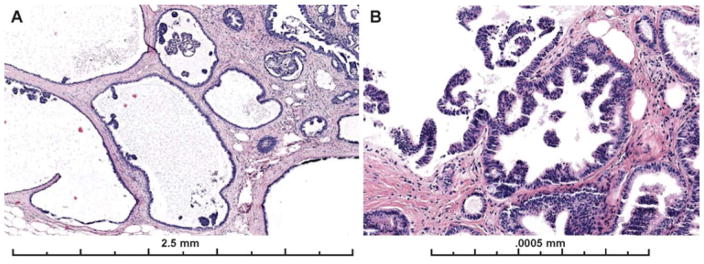
Figure 7.
Examples images from two cases with micropapillary architecture, which was associated with worse diagnostic agreement with the expert consensus diagnosis of ADH. A) Only 28% of participants recorded a diagnosis of ADH on this case, 45% recorded a LN (there was LN also present in multiple foci elsewhere on the slide), 28% recorded a DCIS diagnosis and 0% recorded a Benign diagnosis (29 interpretations). B) Only 24% of participants recorded this case as ADH, with 31% as Benign (mostly columnar cell hyperplasia and UDH), 21% recording the case as FEA and 24% as DCIS (29 total interpretations). Both lesions have scattered micropapillary, club-shaped structures that are only partially involving dilated spaces involved by FEA. Micropapillary patterns can be subtle and easily missed if focal. In the first case (A), the concurrent diagnosis of lobular neoplasia in multiple areas of the same slide may have been a distractor.