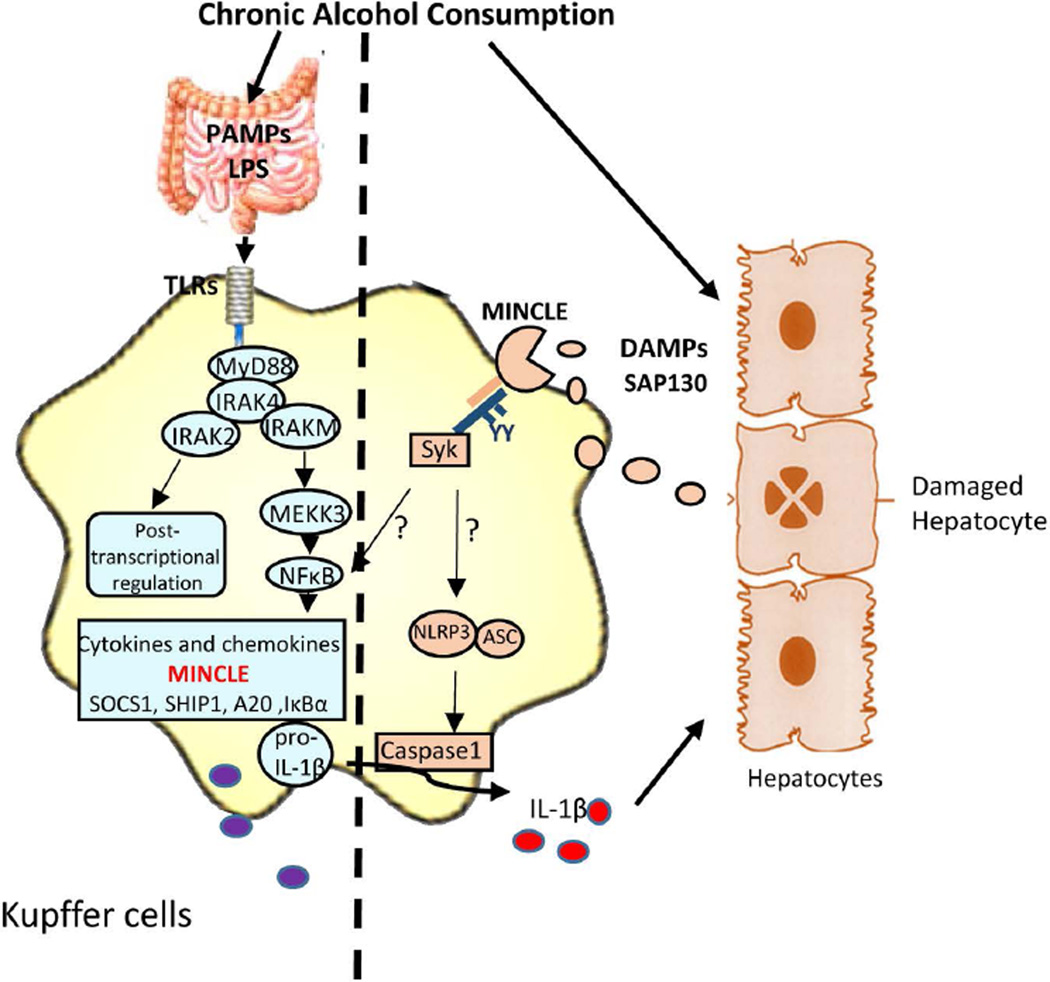
Fig. 7. IRAKM-Mincle axis contributes to the pathogenesis and development of ALD.
Chronic alcohol consumption results in increased intestinal permeability and changes in bacterial microflora increase levels of bacterial products in alcoholic patients and animal models of ALD. Further, alcohol exposure can induce endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in hepatocytes, contributing to hepatocellular injury and death. TLR4- induced IRAKM-mediated MEKK3-dependent NFκB activation is required for the up-regulation of Minlce in hepatic macrophages. Mincle sense the necroptotic hepatocytes-released nuclear protein, SAP130, which in turn activates the inflammasome activation in macrophages. Secreted IL-1β may further act on hepatocytes inducing pyroptosis or on Stellate cells which leads to fibrosis.