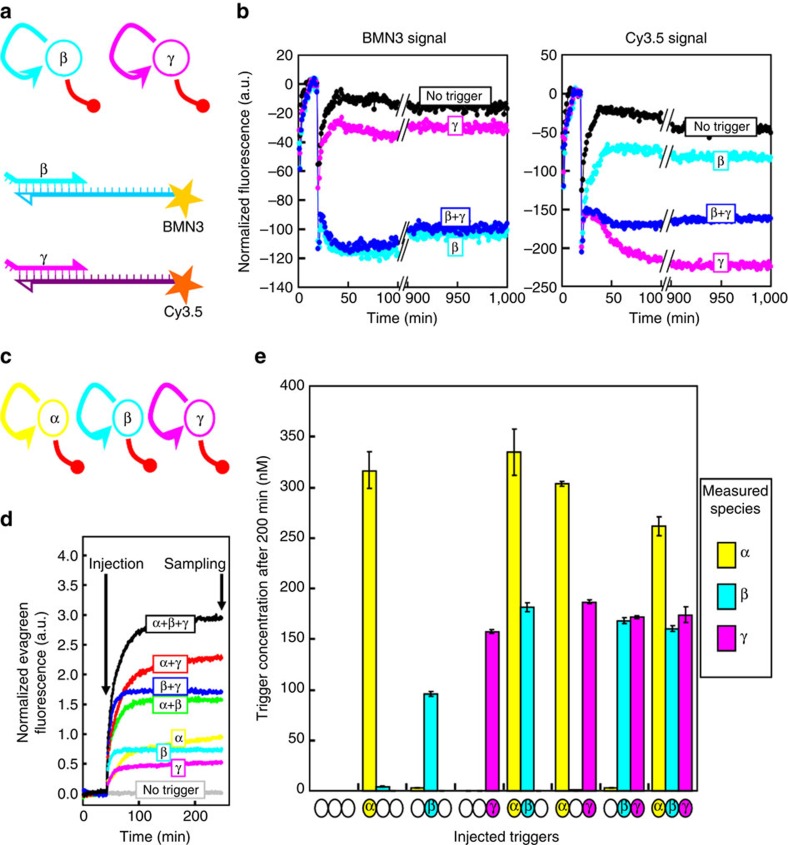
Figure 7. Multistable memory units.
(a) A two-bit system can be constructed by combining two bistable networks with orthogonal sequences, as schematized, and monitored with two fluorescent dyes attached to the templates25. (b) Change over time of BMN3 and Cy3.5 fluorescence after injection of the four possible combinations of the two triggers (no trigger; β only; γ only; β and γ). (c) Similarly, a three-bit system is obtained from three orthogonal nodes. (d) A mixture of αtoα3, βtoβ, γtoγ, drainα1, drainβ and drainγ was triggered with the eight possible combinations of their respective trigger (indicated in the coloured boxes) and EvaGreen fluorescence was monitored for 200 min. The nonspecific fluorescence signal suggests that steady states with one, two or three active nodes are attained. (e) The reaction in each tube from (d) was quenched after 200 min and the concentration of α, β and γ in the mixture were independently measured (see Methods). Only the nodes that had been triggered appeared to be in the high state, while untriggered ones were still in the low state. Each plot shows the mean concentration±s.d. from two measurements.