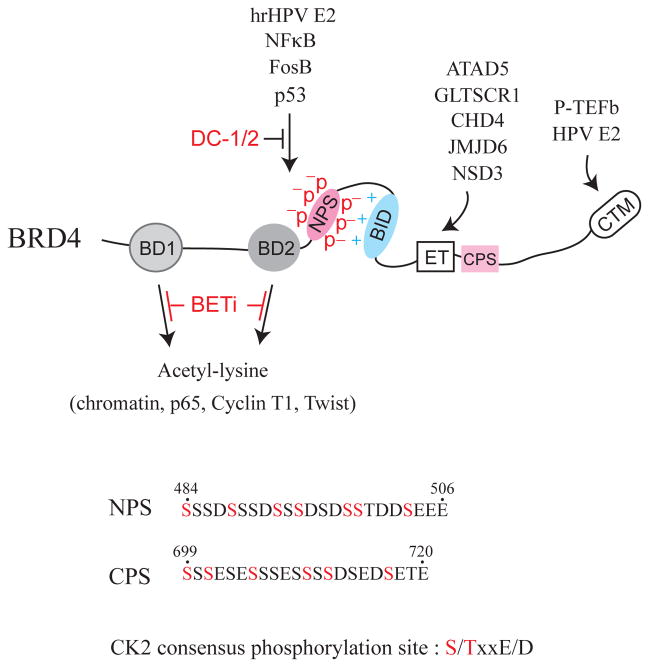
Figure 1.
BRD4 domain features and select interacting factors. Conserved domains shown include bromodomain I (BD1), bromodomain II (BD2), N-terminal cluster of CK2 phosphorylation sites (NPS), basic residue-enriched interaction domain (BID), extraterminal (ET) domain, C-terminal cluster of CK2 phosphorylation sites (CPS), and C-terminal motif (CTM). P indicates phosphorylation, whereas + and − depict positive and negative charge distributions surrounding NPS and BID, respectively. Arrows show factors interacting with individual domains that can be selectively blocked by BET inhibitors (BETi) or DC-1 and DC-2 peptoids. The amino acid sequences of NPS, CPS, and the CK2 consensus phosphorylation site are also listed with potential CK2-phosphorylated serine residues indicated in red. Numbers correspond to the residue positions in the full-length BRD4 protein. hrHPV is an abbreviation for high-risk human papillomavirus.