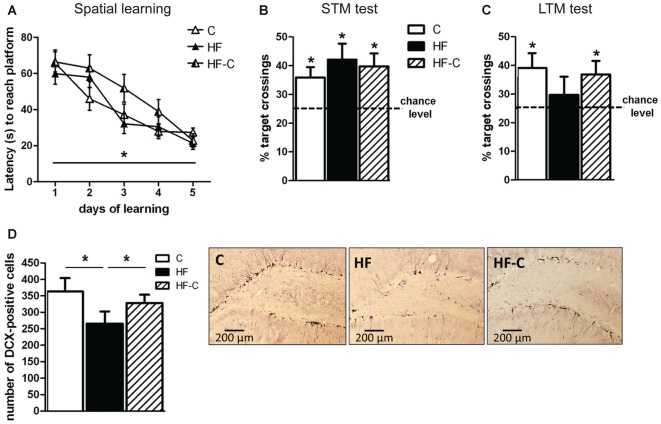
Figure 2.
Spatial hippocampal-dependent memory and hippocampal neurogenesis. (A) Performance in the Morris Water Maze (MWM) across training trials. All groups learned the location of the platform and showed a decreased latency to reach the platform across days. *p < 0.05 (repeated measure’s ANOVA: time effect). (B) Short-term memory (STM) was assessed 2 h after the final training trial. The percentage of target annulus crossing was significantly greater than chance level (25%) for all groups. *p < 0.05 (one-sample t-test). (C) Long-term memory (LTM) was assessed 4 days after the final training session. The percentage of target annulus crossings was significantly greater than chance for groups C (white bar) and HF-C (stripped bar) but not for group HF (black bar). *p < 0.05 (one-sample t-test). (D) Less doublecortin (DCX)-positive cells were observed in the dentate gyrus of group HF than in groups C and HF-C. *p < 0.05 when compared to both C and HF-C groups (significant one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s post hoc). Representative photomicrographs of DCX-immunoreactivity in the dentate gyrus of groups C, HF and HF-C.