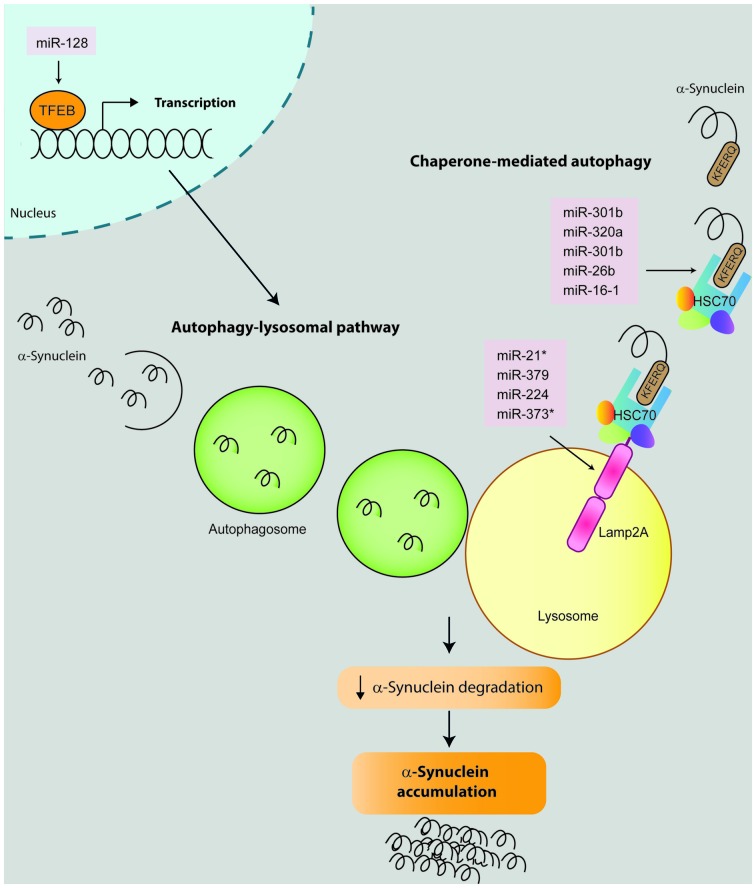
Figure 3.
miRNAs that impact on α-synuclein expression by modulating proteolytic degradation pathways. α-Synuclein can be degraded by several proteolytic pathways including chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) and autophagy-lysosomal pathway (ALP). During the CMA, the KFREQ-like sequence of the α-synuclein protein is recognized by a chaperone complex which includes the Heat shock protein 70 (Hsc70). This complex is guided to the lysosomes and recognized by the Lysosome-associated membrane protein 2 (Lamp2A), which in turn translocate the α-synuclein into the lysosome where it is finally degraded by hydrolytic enzymes. To date, nine microRNAs have been described to modulate the CMA pathway and impact on α-synuclein degradation by directly binding and repressing the expression of Hsc70 (miR-301b, miR-26b, miR-320a, miR-106a and miR-16-1) or Lamp2a (miR-21*, miR-379, miR-373* and miR-224). For ALP degradation, α-synuclein is firstly enclosed into an autophagosome. Then the autophagosome is guided and fused with a lysosome where α-synuclein is finally degraded. In this context, miRNA-128 activates transcription factor EB (TFEB) which has been demonstrated to promote the transcription of genes involved in ALP pathway. Therefore miRNA-repression of Hsc7, Lamp2a or TFEB result in alterations in the α-synuclein degradation and its consequent accumulation.