FIGURE 2.
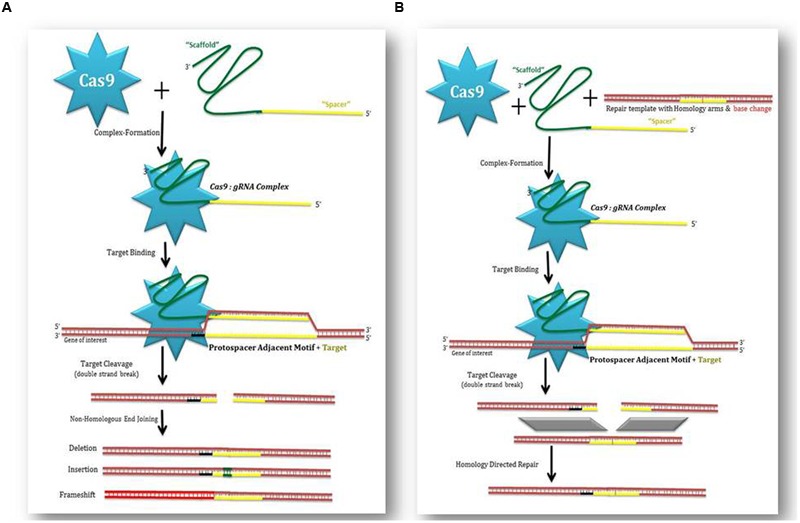
How CRISPR-Cas9 perform genome editing. Cas9 induce double stranded breaks (DSBs) at particular site. The resulting DSB is then repaired by one of these two general repair pathways, e.g., by Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or by Homology directed repair (HDR). (A) The NHEJ repair pathway frequently results in small nucleotide insertions or deletions (InDels) at the DSB site. This may result in gene knock out or gene insertion. (B) HDR can be used to generate precise nucleotide modifications (also called gene “edits”) ranging from a single nucleotide change to large insertions.
