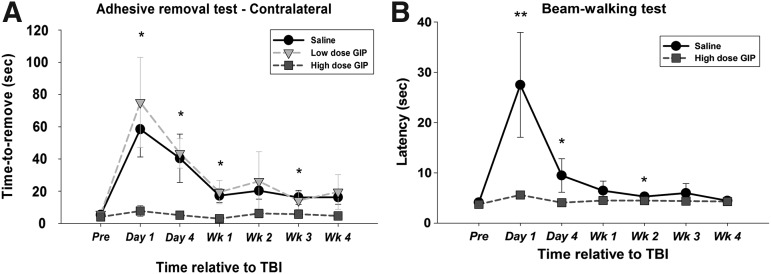
FIG. 4.
The effect of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) on sensory function and gross fine motor coordination were evaluated by the adhesive removal test (A: contralateral limb) and the beam walking test (B) in a temporal analysis. All data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. Compared with vehicle, only the high dose of GIP had a significant difference. **p < 0.01 versus vehicle, *p < 0.05 versus vehicle. TBI, traumatic brain injury.