FIG 3.
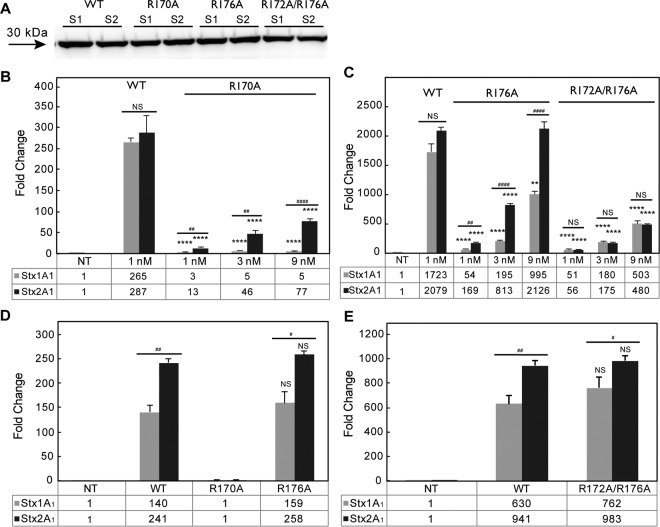
(A) Immunoblot analysis of purified 10×His-tagged WT Stx1A1 and Stx2A1 and 10×His-tagged R170A, R176A, and R172A/R176A variants. Equal amounts (1 μg) of purified Stx1A1 (S1) and Stx2A1 (S2) and variants were separated on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. 10×His-tagged Stx1A1 and Stx2A1 were detected by monoclonal anti-His. (B) Depurination of yeast ribosomes by 10×His-tagged WT Stx1A1 and Stx2A1 and R170A variants. (C) Depurination of yeast ribosomes by 10×His-tagged WT Stx1A1 and Stx2A1 and R176A and R172A/R176A variants. Yeast ribosomes (7 pmol) were incubated with different concentrations of 10×His-tagged WT or variant forms of Stx1A1 or Stx2A1 at 30°C for 10 min. The rRNA (375 ng) was used to quantify the relative levels of depurination by qRT-PCR. The y axis shows the fold change in depurination of toxin-treated samples over the control samples without toxin treatment (NT). The error bars represent SE (n = 3 replicates). The means of WT Stx1A1 and Stx2A1 and their variants were significantly different using a two-sample t test (**, P < 0.01, ****, P < 0.0001 [means compared to the respective WT]; ##, P < 0.01, ####, P < 0.0001 [means compared between Stx1A1 and Stx2A1]; NS, not significant). (D) Depurination of total RNA from yeast by purified Stx1A1, Stx2A1, and R170A and R176A variants. (E) Depurination of total RNA from yeast by purified Stx1A1, Stx2A1, and R172A/R176A variants. Total RNA (1 μg) was incubated with different amounts of 10×His-tagged WT Stx1A1 and Stx2A1 or 10×His-tagged R170A, R176A, and R172A/R176A variants at 37°C for 15 min. The relative levels of depurination were determined using qRT-PCR. The y axis shows the fold change in depurination of toxin-treated samples over the control samples without toxin treatment (NT). The error bars represent SE (n = 3 replicates). The means of Stx1A1, Stx2A1, and their variants were significantly different using a two-sample t test (#, P < 0.05, ##, P < 0.01 [means compared between Stx1A1 and Stx2A1]; NS, not significant).