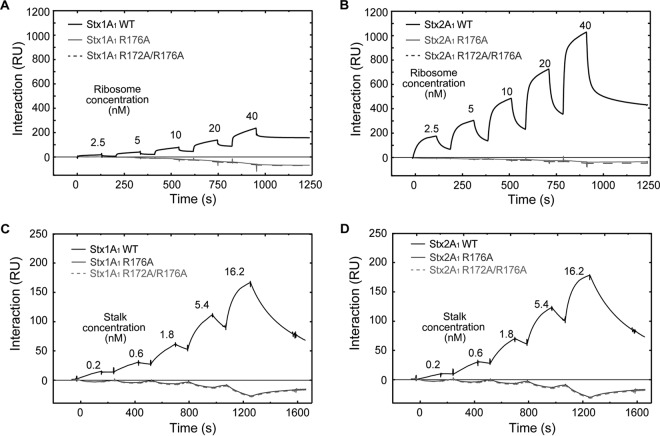
FIG 4.
(A) Interaction of yeast ribosomes with 10×His-tagged WT Stx1A1 and 10×His-tagged R176A and R172A/R176A variants. (B) Interaction of yeast ribosomes with 10×His-tagged WT Stx2A1 and 10×His-tagged R176A and R172A/R176A variants. WT Stx1A1, WT Stx2A1, and R176A and R172A/R176A variants were captured on an NTA chip at 800 RU. Different concentrations of ribosomes were passed over the surface as analytes, as shown. (C) Interaction of the purified yeast stalk pentamer with 10×His-tagged WT Stx1A1 and 10×His-tagged R176A and R172A/R176A variants. (D) Interaction of the purified yeast stalk pentamer with 10×His-tagged WT Stx2A1 and 10×His-tagged R176A and R172A/R176A variants. WT Stx1A1 and Stx2A1 and R176A and R172A/R176A variants were captured on an NTA chip at 1,000 RU, and the same amount of EGFP was captured on the reference channel. Different concentrations of stalk pentamer were passed over the surface as analytes, as shown.