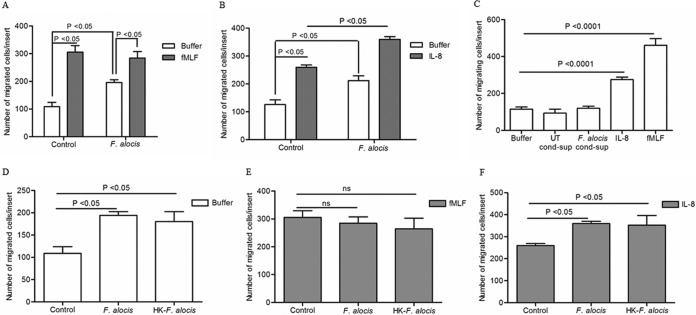
FIG 1.
Effect of F. alocis stimulation on neutrophil chemotaxis. Neutrophils were left unchallenged (control), challenged with F. alocis (30 min), or challenged with heat-killed F. alocis (HK-F. alocis; 30 min). (A to F) Following the bacterial challenge, cells were placed in the upper chamber of the transwell system, and after 30 min of incubation, the membrane was stained with a HEMA 3 stain set kit. Chemotaxis was assessed by light microscopic examination (magnification, ×100). (A) Buffer or fMLF (100 nM) was placed in the lower well. Data are expressed as mean numbers ± standard errors of the mean (SEM) of migrated cells/insert from 9 independent experiments. (B) Buffer or IL-8 (100 ng/ml) was placed in the lower well. Data are expressed as mean numbers ± SEM of migrated cells/insert from 5 independent experiments. (C) Unstimulated cells were placed in the upper chamber of the transwell plate, and buffer, conditioned supernatant collected from unstimulated cells (UT-cond-sup), or conditioned supernatant collected after 60 min of stimulation with F. alocis (F. alocis-cond-sup), IL-8 (100 ng/ml), or fMLF (100 nM) was placed in the lower well. Data are means ± SEM from 6 independent experiments. (D to F) Buffer (D), fMLF (E), or IL-8 (F) was placed in the lower well. Data are expressed as mean numbers ± SEM of migrated cells/insert from 5 independent experiments.