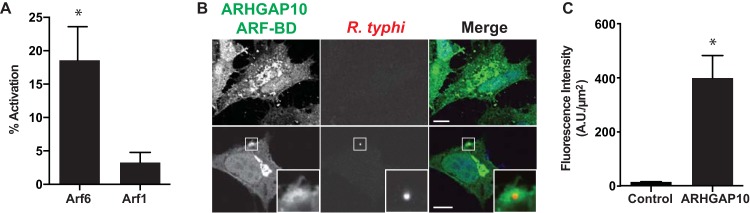
FIG 2.
Arf6 is activated and localized to R. typhi entry foci. (A) Arf6 but not Arf1 is activated early during R. typhi infection. HeLa cells incubated with R. typhi for 30 min were assayed for endogenous Arf6 and Arf1 activation using G-LISA Arf6 and Arf1 Activation Assay Biochem kits (Cytoskeleton). The percentage of activation of Arf6 or Arf1 was calculated in HeLa cells 30 min postinfection with R. typhi (MOI, 100:1) compared to that in uninfected HeLa cells. Arf6, but not Arf1, was significantly activated by R. typhi infection compared to the level in uninfected controls. Error bars represent means ± SEM from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 by Student's two-sided t test. (B) GTP-bound Arf6 localizes to R. typhi entry foci. HeLa cells overexpressing the ARF-binding domain of ARHGAP10 (an Arf6 GTP-bound biosensor) fused to GFP were exposed to R. typhi (MOI, 100:1) for 15 min (bottom panel) or mock treated (top panel). Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and R. typhi was detected with anti-R. typhi Ab (red). DAPI (blue) is shown in the merged image. Boxed regions are enlarged to show detail. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Quantification of ARHGAP10 Arf-BD localization at the R. typhi entry foci. Cells expressing GFP-tagged ARHGAP10 Arf-BD or GFP alone were infected with R. typhi and processed as described for panel B. Fluorescence immediately surrounding R. typhi was measured using ImageJ (NIH) and expressed as arbitrary units (A.U.) per square micrometer. The means ± SEM of 10 to 15 bacteria from two independent experiments are plotted. *, P < 0.05 by Student's two-sided t test.