FIG 4.
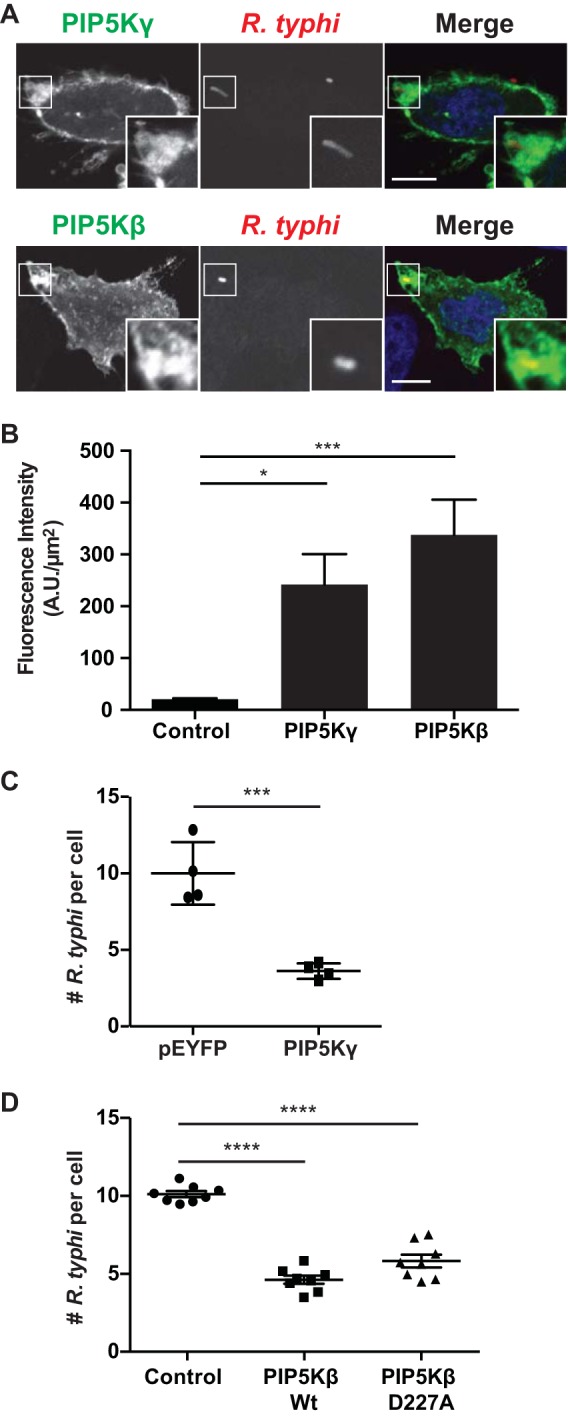
PIP5K is recruited to R. typhi entry foci. (A) HeLa cells overexpressing GFP-PIP5Kγ (top) or HA-PIP5Kβ (bottom) were incubated with R. typhi (MOI, 100:1) for 15 min. Cells were fixed with 4% PFA, and R. typhi cells were detected with rat anti-R. typhi serum and anti-rat Alexa Fluor 594 (red). HA-tagged PIP5Kβ was detected with a mouse anti-HA antibody followed by anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 antibody (green). DAPI (blue) is shown in the merged image. Boxed regions are enlarged to show detail. Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) Quantification of PIP5K localization at the R. typhi entry foci. GFP-, GFP-PIP5Kγ-, or HA-PIP5Kβ-expressing cells were infected with R. typhi and processed as described for panel A. Fluorescence immediately surrounding R. typhi was measured using ImageJ (NIH) and expressed as arbitrary units (A.U.) per square micrometer. The means ± SEM of 10 to 15 bacteria from two independent experiments are plotted. *, P < 0.05, and ***, P < 0.0001, by one-way ANOVA and Dunnett's multiple-comparison test. (C) Overexpression of PIP5Kγ decreases R. typhi infection. HeLa cells expressing GFP alone or GFP-PIP5Kγ were incubated with R. typhi (MOI, 100:1) for 2 h. Cells were fixed with 4% PFA, and R. typhi was detected with rat anti-R. typhi serum and anti-rat Alexa Fluor 594. The number of R. typhi bacteria per cell for 100 cells was calculated for four independent experiments, and means ± SEM are plotted. ***, P < 0.001 by Student's two-sided t test. (D) Overexpression of wild-type and catalytically dead PIP5Kβ decreases R. typhi infection. HeLa cells expressing the HA-tagged PIP5Kβ wild-type (wt) or catalytically dead mutant (D227A) were exposed to R. typhi (MOI, 100:1) for 2 h. Cells were fixed with 4% PFA, R. typhi bacteria were detected with rat anti-R. typhi serum, and HA-tagged PIP5Kβ was detected with mouse anti-HA antibody. The number of R. typhi bacteria per cell for 100 cells in four different wells per condition was calculated for three independent experiments, and means ± SEM are plotted. ****, P < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA and Dunnett's multiple-comparison test.
