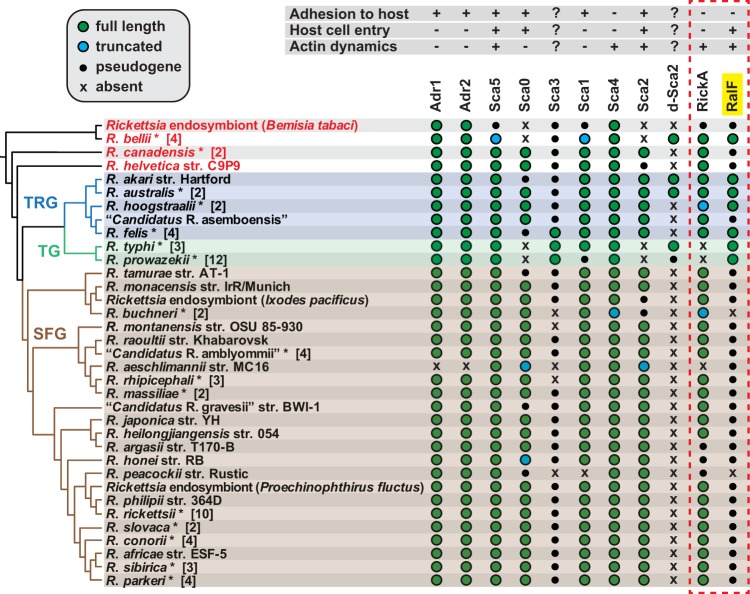
FIG 6.
Phylogenomic analysis of Rickettsia proteins implicated in host cell invasion. The phylogeny at left, which includes 82 Rickettsia genomes, was estimated as previously described (44, 72). The inset at the top left describes gene characteristics: green, full length; blue, truncated; black, pseudogene; x, absent. Taxonomic groups (73) are as follows: TRG, transitional group rickettsiae; TG, typhus group rickettsiae; SFG, spotted fever group rickettsiae. Red taxa depict ancestral lineages. Taxa with asterisks are a composite of multiple genomes from the same species, with numbers in brackets indicating the total number of genomes analyzed. In some cases where different strains show variation for a particular gene, the characteristics of the gene from the better-quality genome were selected. Note that some composite taxa include genomes from attenuated strains (e.g., R. prowazekii strain Madrid E and R. rickettsii strain Iowa) that contain different genetic profiles than those listed. The dashed red box distinguishes the two rickettsial effectors from the nine adhesins, with RalF highlighted in yellow.