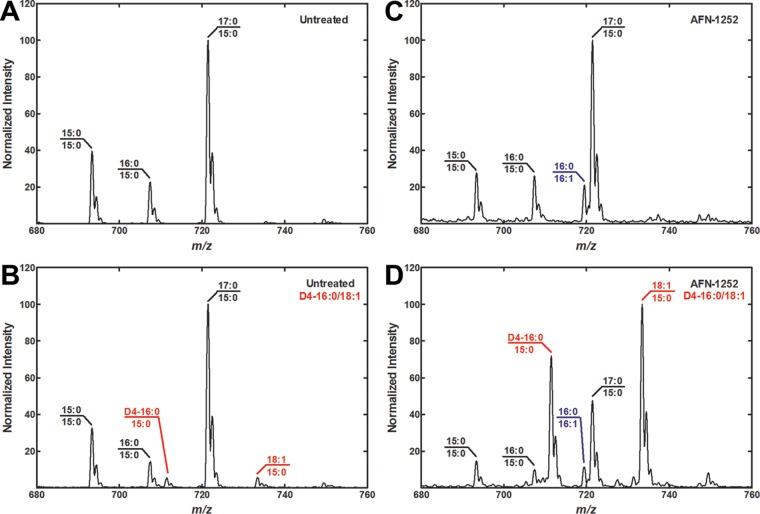
FIG 4.
Exogenous fatty acid metabolism in L. monocytogenes. Growing cultures of untreated or AFN-1252 (50 μM)-treated L. monocytogenes in tryptic soy broth medium were not supplemented with exogenous fatty acids or were supplemented with straight-chain fatty acid (100 μM D4-16:0 and 100 μM 18:1) and grown to an A600 of ≈1.5. The lipids were harvested from the cells and the PG molecular species were determined. The identities of the major molecular species are annotated in the figure, and the new molecular species arising from the incorporation of the fatty acid supplements are highlighted in red. New molecular species (16:0/16:1) arising from incorporation of fatty acids present in tryptic soy broth are highlighted in blue. Spectra shown are representative examples from two biological replicates. (A) PG molecular species profile of L. monocytogenes with no drug treatment and no fatty acid supplementation. (B) PG molecular species profile of L. monocytogenes with no drug treatment and straight-chain fatty acid supplementation. (C) PG molecular species profile of L. monocytogenes with AFN-1252 treatment and no fatty acid supplementation. (D) PG molecular species profile of L. monocytogenes with AFN-1252 treatment and straight-chain fatty acid supplementation.