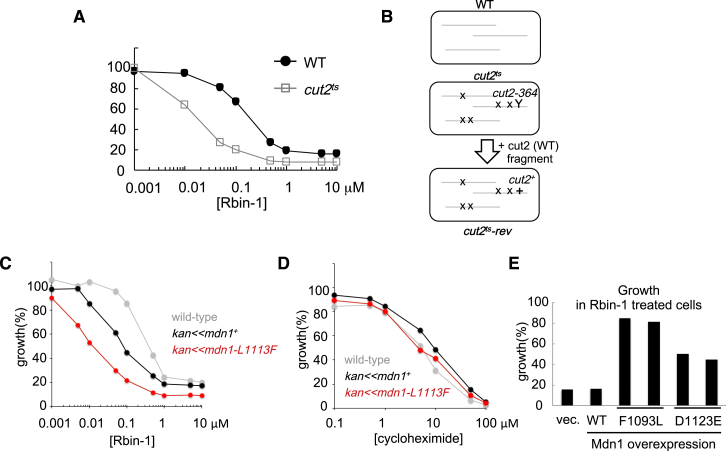
Figure S1.
Analysis of Rbin-1-Sensitive and -Resistant mdn1 Mutants, Related to Figure 1
(A) The cut2-364 (cut2ts) strain shows higher sensitivity to Rbin-1 than wild-type (WT). Exponentially growing culture (OD = 0.5) of WT (black circle) and cut2ts (gray square) cells were diluted 50 times in YE4S medium and treated with Rbin-1, and incubated for 17 hr at 29°C. Growth (%) is presented relative to DMSO-treated cells.
(B) Schematic shows potential difference between wild-type (WT) and cut2-364 (cut2ts) strains. X indicates background mutations in cut2-364 strain. Y indicates a mutation in the cut2 gene. “cut2ts-rev” strain was constructed by utilizing homologous recombination between cut2-364 mutation and cut2 (WT) fragments.
(C and D) A point mutation in the mdn1 gene (L1113F) confers Rbin-1 sensitivity. Exponentially growing culture (OD = 0.5) of wild-type (square), kan < < mdn1+ (triangle), and kan < < mdn1 (L1113F) (circle) cells were diluted 50 times in YE4S medium and treated with RBin-1(C) or cycloheximide (D), and incubated for 17 hr at 29°C. Growth (%) is presented relative to DMSO-treated cells.
(E) Overexpression of Mdn1 mutants (F1093L or D1123E) confers Rbin-1 resistance. Exponentially growing culture of MDR-sup strains, in which wild-type (WT) or mutants (F1093L or D1123E) of full-length Mdn1, or vector control (-) were overexpressed (from the nmt1 promoter), were diluted 25 times in EMM-L medium and treated with 1 μM Rbin-1, and incubated for 18.5 hr at 32°C. Growth (%) is presented relative to DMSO-treated cells.