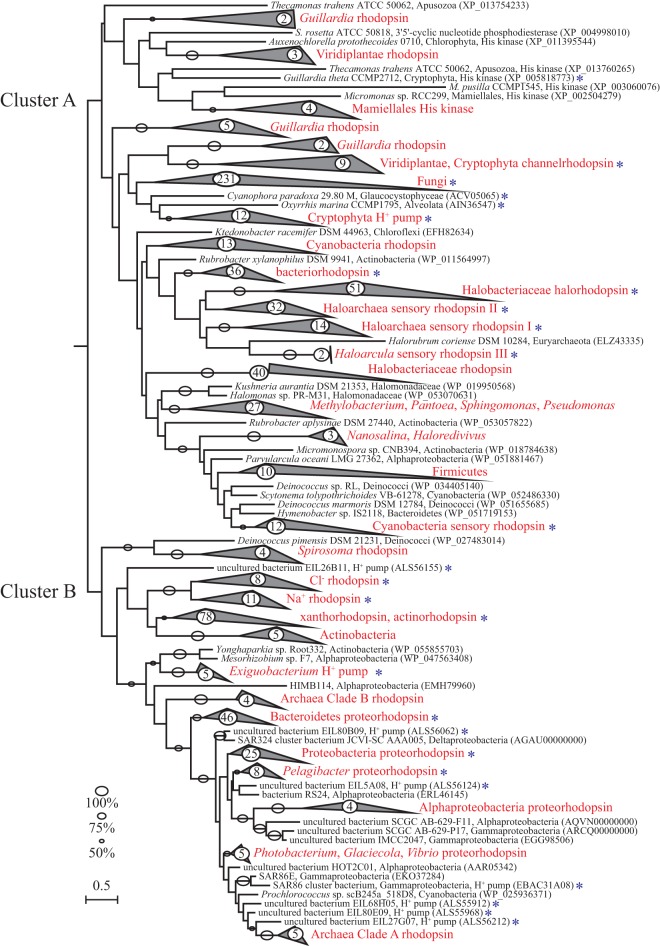
FIG 2.
Phylogenetic relationships of rhodopsins. An unrooted tree of rhodopsins from the three domains of life is shown. A total of 756 rhodopsin sequences were downloaded from RefSeq (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/refseq/; release 75, 14 March 2016), following identification using the PFAM for bacteriorhodopsin-like protein (Bac_rhodopsin, PF01036). The sequences were aligned using MUSCLE and further edited with Gblocks to eliminate highly divergent regions. The tree was constructed by the maximum-likelihood method using the LG model of amino acid substitution rates with empirical amino acid frequencies and the gamma model of rate heterogeneity (PROTGAMMALGF) in RAxML. Bootstrap support values higher than 50% are shown above branches based on 100 pseudoreplicates. Only the region of the peptide that spans the PFAM protein family specific for rhodopsin was considered in the alignment. GenBank accession numbers are shown in parentheses for the individual sequences. Blue asterisks indicate individual organisms for which there is experimental evidence for the function of the rhodopsin; in the case of collapsed branches (marked in red), asterisks indicate that there is experimental evidence for at least one organism. Numbers within circles are the number of sequences in the collapsed branches. The scale bar represents substitutions per site.