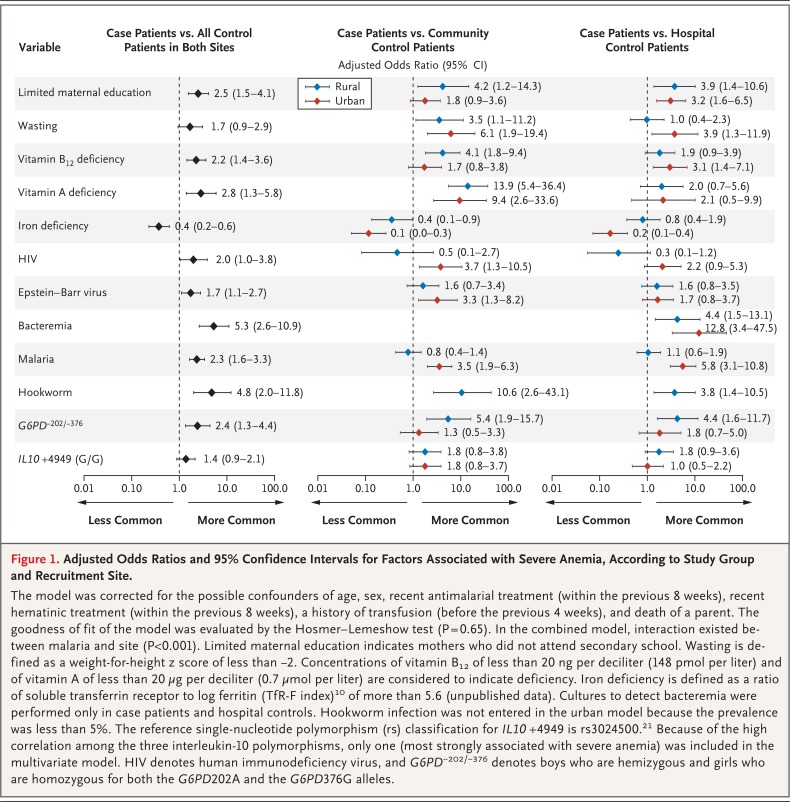
Figure 1.
Adjusted Odds Ratios and 95% Confidence Intervals for Factors Associated with Severe Anemia, According to Study Group and Recruitment Site.
The model was corrected for the possible confounders of age, sex, recent antimalarial treatment (within the previous 8 weeks), recent hematinic treatment (within the previous 8 weeks), a history of transfusion (before the previous 4 weeks), and death of a parent. The goodness of fit of the model was evaluated by the Hosmer-Lemeshow test (P = 0.65). In the combined model, interaction existed between malaria and site (P<0.001). Limited maternal education indicates mothers who did not attend secondary school. Wasting is defined as a weight-for-height z score of less than −2. Concentrations of vitamin B12 of less than 20 ng per deciliter (148 pmol per liter) and of vitamin A of less than 20 µg per deciliter (0.7 µmol per liter) are considered to indicate deficiency. Iron deficiency is defined as a ratio of soluble transferrin receptor to log ferritin (TfR-F index)10 of more than 5.6 (unpublished data). Cultures to detect bacteremia were performed only in case patients and hospital controls. Hookworm infection was not entered in the urban model because the prevalence was less than 5%. The reference single-nucleotide polymorphism (rs) classification for IL10 +4949 is rs3024500.21 Because of the high correlation among the three interleukin-10 polymorphisms, only one (most strongly associated with severe anemia) was included in the multivariate model. HIV denotes human immunodeficiency virus, and G6PD−202/−376 denotes boys who are hemizygous and girls who are homozygous for both the G6PD202A and the G6PD376G alleles.