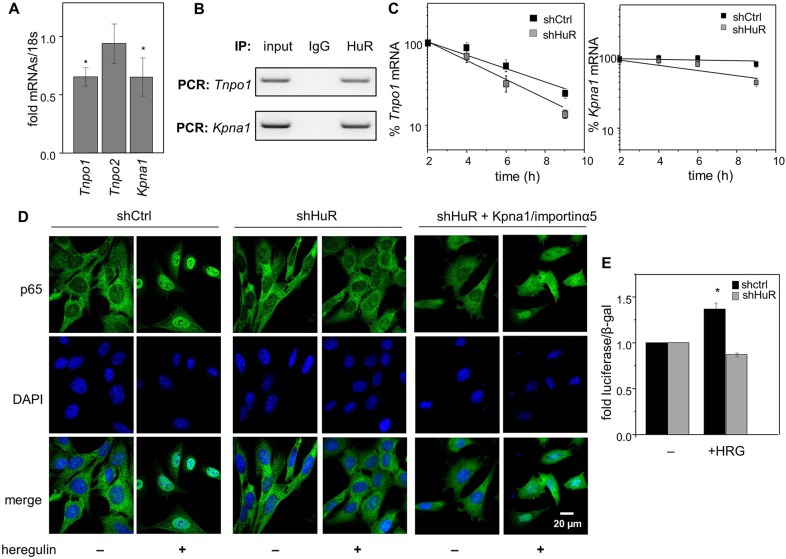
Fig. 7.
Stabilization of Tnpo1 and Kpna1 mRNAs by HuR contributes to its ability to control the nuclear import of p65. (A) Levels of mRNA for Tnpo1/importin-β1, Tnpo2 and Kpna1/importin-α5 in M2−/− cells stably expressing shCtrl or shHuR, as measured by Q-PCR and normalized to 18s. Levels of mRNAs in shHuR-expressing cells normalized to cells expressing shCtrl are shown (mean±s.d.; n=3). *P<0.05, paired Student's t-test, compared to cells expressing shCtrl. (B) HuR was immunoprecipitated from M2−/− cells. Tnpo1 and Kpna1 mRNAs that co-precipitated with HuR were detected by semi-quantitative PCR. (C) Cells were treated with actinomycin D (2.5 µg/ml) and levels of Tnpo1 (left) and Kpna1 (right) mRNAs at various time points were measured by Q-PCR. Data were normalized to corresponding values at time zero (mean±s.e.m.; n=3). (D) M2−/− cells stably expressing shCtrl or shHuR and shHuR-expressing cells transfected with a vector encoding importin-α5 were treated with vehicle or heregulin-β1 (0.1 µg/ml) for 30 min. p65 was immunostained and visualized. DAPI was used to visualize nuclei. (E) Transactivation assays in denoted cells transfected with a vector harboring a luciferase reporter driven by 800 bp of the proximal promoter of FABP5. Cells were serum starved and treated with vehicle or heregulin-β1 (HRG; 50 ng/ml, overnight). Luciferase activity was measured and normalized to β-galactosidase (means±s.d.; n=3). *P<0.05, paired Student's t-test, compared to vehicle-treated cells.