Fig. 3.
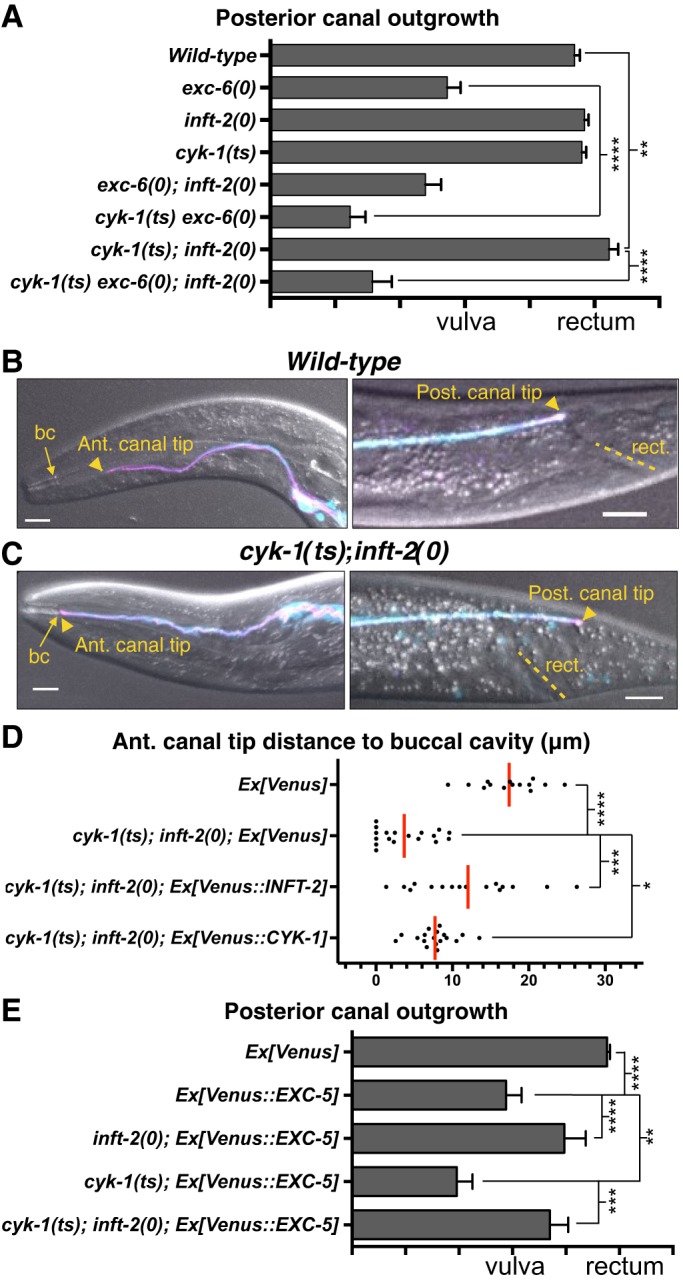
INFT-2 and CYK-1 regulate EC outgrowth. (A) Genetic interactions between exc-6, inft-2 and cyk-1. Analysis of all genotypes shown in this figure (see Table S1) was performed by applying a temperature shift to achieve strong reduction of CYK-1 function in cyk-1(ts) mutants, as described in the main text and in Materials and Methods. For each genotype, n≥76 canal arms were scored. Concomitant loss of EXC-6 and CYK-1 causes a strong synergistic effect, similar to that seen in exc-6(0); exc-5(0) and cdc-42(0*); exc-6(0) double mutants (Fig. 1G). Single inft-2(0) and cyk-1(ts) mutants do not display outgrowth defects, but the cyk-1(ts); inft-2(0) double displays significant overgrowth that is overcome by loss of exc-6. (B,C) In a wild-type background (B), the anterior (Ant.) canal terminates well before reaching the buccal cavity (bc) and the posterior (Post.) canal terminates at the rectum (rect.) whereas in cyk-1(ts); inft-2(0) hermaphrodites (C) there is significant overgrowth. (D) Quantification of anterior canal overgrowth in cyk-1(ts); inft-2(0) double mutants, and rescue by Venus-tagged INFT-2 (arEx2406) and CYK-1 (arEx2410). Each dot represents the distance (in µm) from the tip of an anterior canal arm to the buccal cavity, with the red bar representing the mean of all measurements. (E) Loss of INFT-2 suppresses, whereas loss of CYK-1 exacerbates, the defects caused by Venus::EXC-5 overexpression (arEx2360). In the triple combination, the outgrowth phenotype is not significantly different from that of inft-2(0); Ex[Venus::EXC-5] double mutants. For each genotype, n≥60 canal arms were scored. Scale bars: 10 µm.
