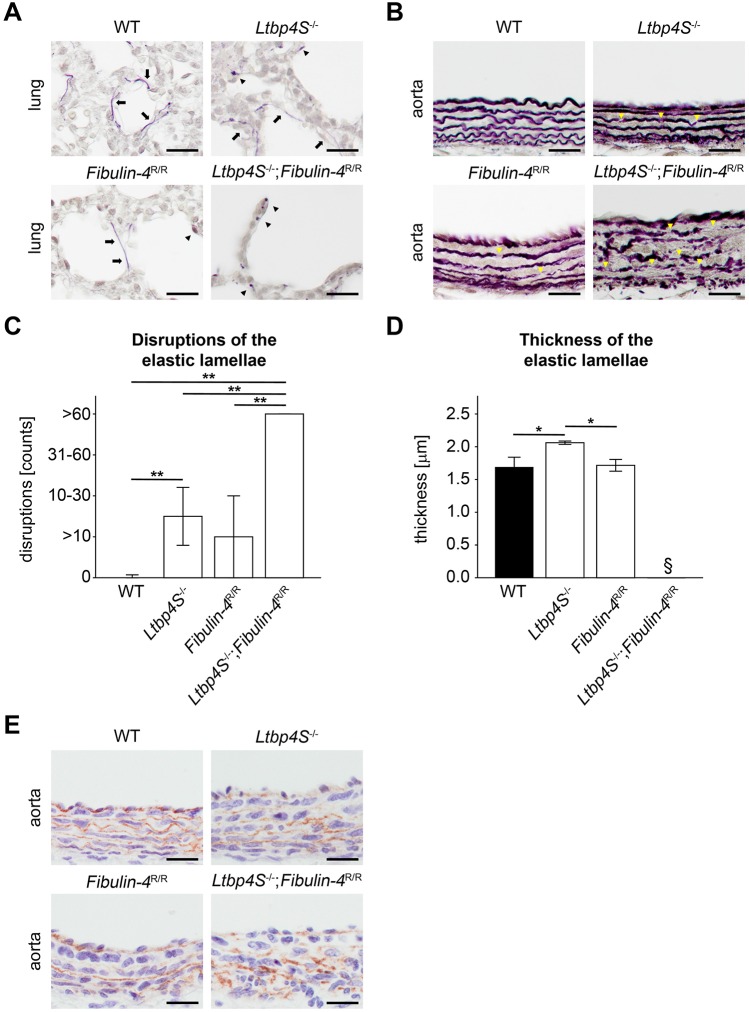
Fig. 2.
Impaired elastogenesis in Ltbp4S−/−;Fibulin-4R/R mice with reduced interaction of Ltbp-4L and fibulin-4. (A) Representative histochemical elastica stainings of lungs showed intact elastic fibers (arrows) in WT mice. In Ltbp4S−/− and Fibulin-4R/R mice, elastic fibers were composed of both intact fibers (arrows) and scattered patches of elastin aggregates (arrowheads). Elastic fibers were severely fragmented (arrowheads) in Ltbp4S−/−;Fibulin-4R/R mice (scale bars: 20 µm). (B) Representative histochemical elastica stainings of abdominal aortas showed occasional disruptions (yellow arrowheads) in Fibulin-4R/R mice and moderate elastic fiber fragmentations (yellow arrowheads) in Ltbp4S−/− mice. In Ltbp4S−/−;Fibulin-4R/R mice, elastic fibers were severely fragmented (yellow arrowheads) (scale bars: 20 µm). (C) Quantitative analysis of disruptions of the medial elastic lamellae showed significantly higher numbers of disruptions in Ltbp4S−/− abdominal aortas compared to WT abdominal aortas and significantly higher numbers of disruptions in Ltbp4S−/−;Fibulin-4R/R aortas compared to all other genotypes (n=3; **P<0.01). (D) Quantitative analysis of the thickness of the medial elastic lamellae showed significantly thicker elastic lamellae in Ltbp4S−/− abdominal aortas compared to WT and Fibulin-4R/R abdominal aortas. The thickness of the medial elastic lamellae could not be determined in Ltbp4S−/−;Fibulin-4R/R abdominal aortas (n=3; *P<0.05; §not determinable). (E) Representative images showed fibulin-5 immunoreactivity and disruption of the fibrillar structure of fibulin-5 fibers in abdominal aortas of Ltbp4S−/− and Ltbp4S−/−;Fibulin-4R/R mice compared to WT and Fibulin-4R/R abdominal aortas (scale bars: 20 µm). Data are presented as means±s.d.; n indicates the number of analyzed tissue of individual mice. Differences between groups were analyzed by two-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni correction.