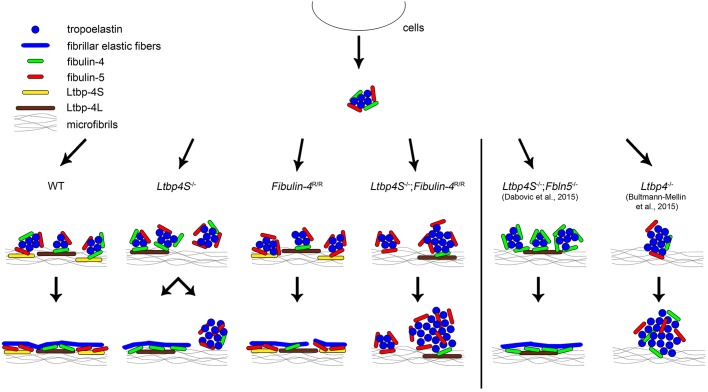
Fig. 3.
Proposed model for the role of Ltbp-4L, Ltbp-4S, fibulin-4 and fibulin-5 in elastogenesis. Normal elastogenesis in WT mice: proper elastic fiber assembly requires microaggregation of tropoelastin linked to fibulin-4 and fibulin-5 followed by binding of this complex to Ltbp-4L and Ltbp-4S and its linear deposition onto fibrillin microfibrils. Ltbp-4L might favor the interaction with fibulin-4 and Ltbp-4S with fibulin-5. The subsequent coalescence of tropoelastin results in fibrillar elastic fibers. Ltbp4S−/− mice: fibulin-4, as part of the tropoelastin complex, binds to Ltbp-4L, resulting in scattered fibrillar elastic fibers. Fibulin-5 cannot bind to Ltbp-4S, which leads to amorphous, non-fibrillar elastin aggregates. Fibulin-4R/R mice: if fibulin-4 expression is reduced (10% remaining expression), elastic fibers display occasional disruptions, most likely because fibulin-5 cannot compensate for the partial loss of fibulin-4. Ltbp4S−/−;Fibulin-4R/R mice: if only Ltbp-4L is expressed and fibulin-4 expression is reduced, elastogenesis is severely impaired. Elastic fibers are severely fragmented and no intact fibers are observed. Ltbp4S−/−;Fbln5−/− mice: if only Ltbp-4L is expressed and fibulin-5 expression is missing, an alternative elastogenesis pathway most likely involving direct interaction of Ltbp-4L and fibulin-4 leads to the formation of fibrillar elastic fibers (Dabovic et al., 2015). Ltbp4−/− mice: if Ltbp-4L and Ltbp-4S are missing, only amorphous, non-fibrillar globular elastin structures instead of fibrillar elastic fibers are present (Bultmann-Mellin et al., 2015). Modified from Bultmann-Mellin et al. (2015), Dabovic et al. (2015) and Noda et al. (2013).