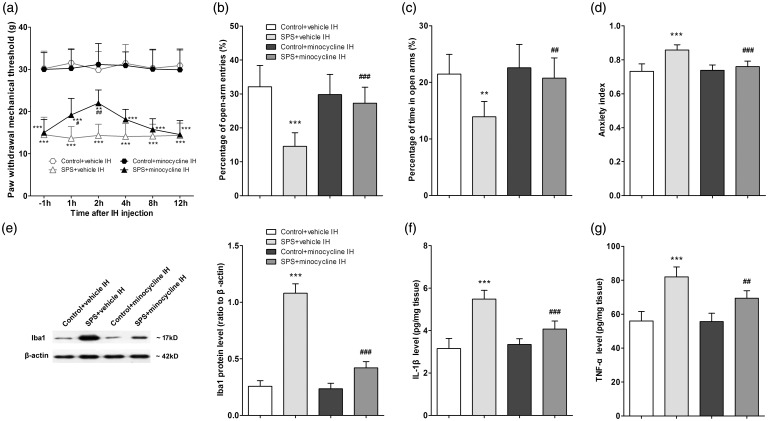
Figure 5.
Intra-hippocampal (IH) injection of minocycline suppressed single prolonged stress (SPS)-induced hippocampal microglia activation and attenuated SPS-induced mechanical allodynia and anxiety-like behavior. (a) Pain sensitivity was determined by measuring paw withdrawal mechanical threshold (PWMT) at 1 h before and at 1, 2, 4, 8, and 12 h after IH injection on the day after SPS (n = 8 in each group). Anxiety-like behavior was tested in the EPM at 2 h after IH injection on the day after SPS. Percentage (%) of open-arm entries (b) and time spent in the open arms (c) as well as anxiety index (d) were calculated (n = 8 in each group). (e) Iba1 protein levels in the hippocampus were measured using Western blot analysis, and hippocampal levels of IL-1β (f) and TNF-α (g) were measured using enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay analysis (n = 5 in each group). Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with group control + vehicle IH; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 compared with group SPS + vehicle IH.