Fig. 4.
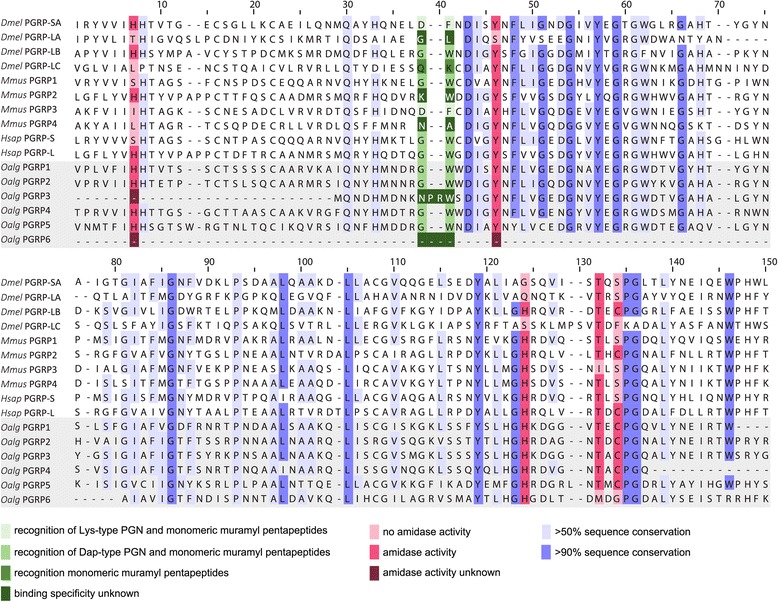
Protein alignment of peptidoglycan recognition proteins. Protein alignment of PGRP domain sequences from different model organisms and Olavius algarvensis; Dmel Drosophila melanogaster (GenBank accession numbers: PGRP-SA, Q9VYX7; PGRP-LA, Q95T64; PGRP-LB, Q8INK6; PGRP-LC, Q9GNK5), Mmus Mus musculus (GenBank accession numbers: PGRP1, O88593; PGRP2, Q8VCS0; PGRP3, A1A547; PGRP4, Q0VB07), Hsap Homo sapiens (GenBank accession numbers: PGRP-S, O75594; PGRP-L, Q96PD5), Oalg Olavius algarvensis (OalgPGRP1, comp330541_c4; OalgPGRP2, comp250229_c0; OalgPGRP3, comp335695_c10; OalgPGRP4, comp314994_c0; OalgPGRP5, comp332570_c2; OalgPGRP6, comp1100768_c0). Conserved active-site residues that confer amidase activity are shown in red; mutation of at least one active-site residue (pink) removes amidase activity
