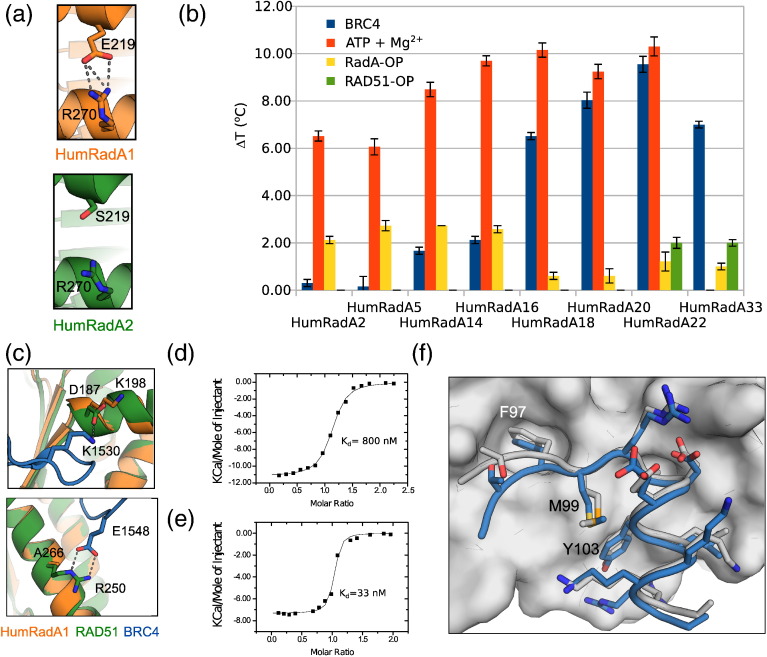
Fig. 2.
Humanisation of RadA and validation of mutants with different ligands. (a) Details of ionic interaction between E219 and R270 in HumRadA1 (orange) and the equivalent residues in HumRadA2 (green), causing reduction in the thermal stability of the protein. (b) Thermal shift analyses of different HumRadA mutants in the presence of BRC4 (blue), RadA-OP (yellow), and RAD51-OP (green) peptides and with ATP-Mg2 + (red). (c) Mutations A266R250 and K198D187 (introduced in HumRadA16 and HumRadA18, respectively) reinstate the interactions existing in the HsRAD51:BRC4 complex that promote the tight binding of the peptide. RAD51 structure is shown in green and RadA in orange, with BRC4 repeat in blue. RAD51 structure is shown in green and RadA in orange, with BRC4 repeat in blue. (d) Binding isotherm of ITC titration of RAD51 oligomerisation peptide into HumRadA33. (e) Binding isotherm of ITC titration of BRC4 peptide into HumRadA33. ITC data for other peptide binding ITC measurements are found in Fig. S3. (f) Structure of HumRadA1 in complex with RadA-OP peptide. The peptide (in blue) is shown as sticks on the HumRadA2 molecular surface. The white sticks show the corresponding region of the oligomerisation sequence from PfRadA heptameric structure (PDB: 1PZN, chain A).