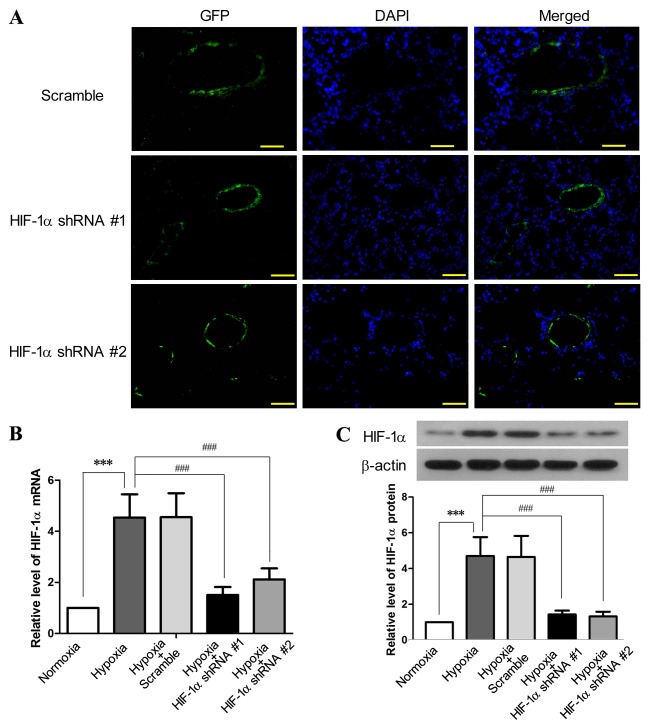
Figure 1.
Lentivirus-mediated delivery of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) shRNA to pulmonary arteries inhibits the hypoxia-induced upregulation of HIF-1α. SD rats received EGFP-encoding lentiviruses carrying HIF-1α shRNA #1, HIF-1α shRNA #2 or scramble shRNA by intratracheal instillation for 6 days, followed by exposure to hypoxia (10% O2) for 3 weeks. SD rats without lentiviral treatment were exposed to hypoxia or normoxia for 3 weeks as the control (n=6 for each group). (A) Following exposure to hypoxia, the cryosections of the lungs from the rats receiving lentiviral treatment were prepared and examined under a fluorescence microscope (×200 magnification; scale bar, 100 µm) to detect the expression of green fluorescence protein (GFP), which was primarily aligned with the pulmonary vessels. Following lentiviral treatment and exposure to hypoxia, the rats were sacrificed and the pulmonary arteries were isolated. The levels of (B) HIF-1α mRNA and (C) HIF-1α protein in the pulmonary arteries were assessed by RT-qPCR and western blot analysis, respectively. This figure shows the representative images from each group, and the values are expressed as the means ± SD. ***P<0.001, hypoxia vs. normoxia; ###P<0.001, hypoxia + HIF-1α shRNAs vs. hypoxia.