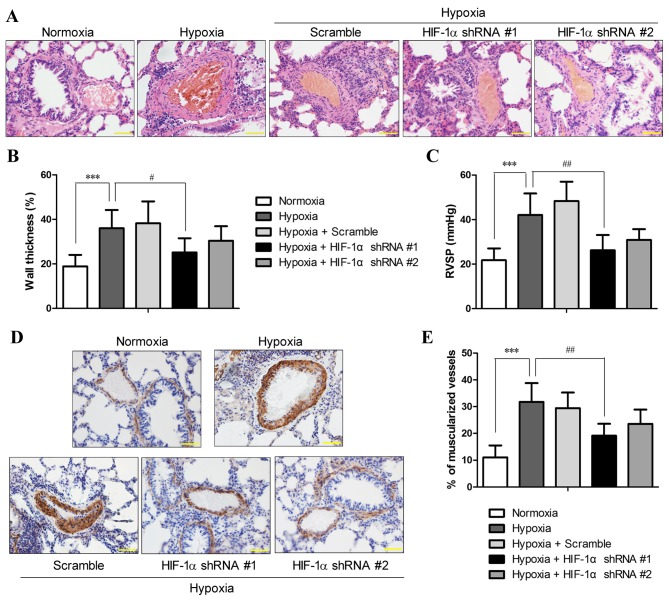
Figure 2.
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) shRNA pre-treatment reduced hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH) and pulmonary arterial remodeling. SD rats with and without pre-treatment of HIF-1α shRNA were exposed to hypoxia for 3 weeks. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of the lung sections were performed, and the sections were examined microscopically under a 400× lens (scale bar, 50 µm). (B) The external diameter and internal diameter of the arteries were measured based on H&E images using ImageJ software, and the percentage wall thickness was calculated as described in the Materials and methods. (C) Following exposure to hypoxia or normoxia, right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) was measured. (D) The degree of muscularization of pulmonary arteries was assessed by immunohistochemical staining for α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) in the lung sections. The images were photographed at ×400 magnification (scale bar, 50 µm), and (E) the percentage of fully muscularized vessels was statistically analyzed based on 60–80 vessels/rat. The figure shows the representative images from each group (n=6/group), and the values are expressed as the means ± SD. ***P<0.001, hypoxia vs. normoxia;; #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01, hypoxia + HIF-1α shRNAs vs. hypoxia.