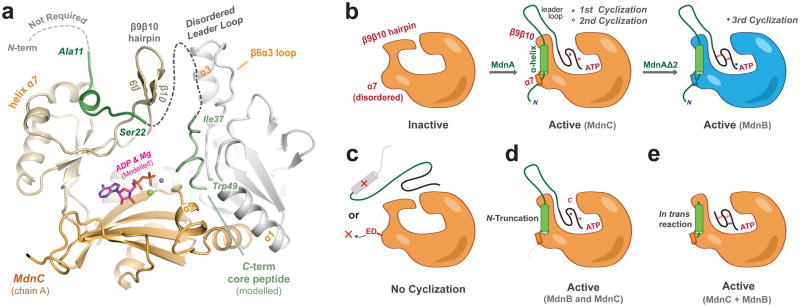
Figure 5. Leader peptide directed peptide macrocyclization in the microviridin J biosynthetic pathway.
(a) Model of the interactions of full length MdnA (green) with the macrocyclase, MdnC. The cyclized core peptide region was adapted from pdb entry 4KTU and docked into MdnC with modelled ADP. (b) The leader peptide of MdnA activates macrocyclation by orienting α7 and by inducing a large shift of the β9β10 hairpin. (c) The α-helical element of the precursor peptide, as well as residues on α7 (Glu191/Asp192, ‘ED’), are critical and removing these elements result in no cyclization, (d) whereas the N-terminus of the substrate is not requisite for either MdnB or MdnC macrocyclizations. (e) In trans activation of MdnC using the α-helical element of the precursor peptide and an inactive substrate produces fully active macrocyclases.