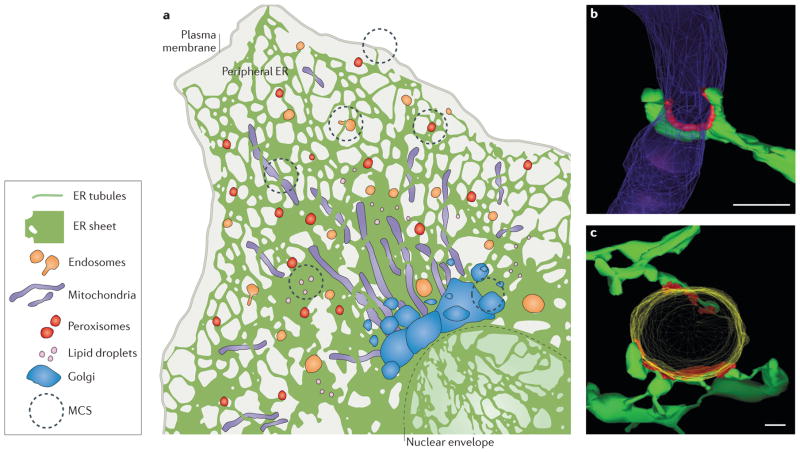
Figure 1. Structure of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane-contact sites (MCSs).
a | The ER consists of the nuclear envelope (outlined with a dashed line) and the peripheral ER, which spreads into the cytosol as a network of sheets and tubules. The peripheral ER forms MCSs with the plasma membrane, mitochondria, endosomes, peroxisomes, lipid droplets and the Golgi. b, c | Electron tomography reveals the three-dimensional structure of MCSs (coloured red) between ER tubules (green) and mitochondria (purple) in a yeast cell b) or an endosome (yellow) in an animal cell (c). Scale bars represent 200 nm in parts b–c. Image in parts b reproduced with permission from REF. 9, AAAS. Image in part c republished with permission of the American Society for Cell Biology, from Endoplasmic reticulum-endosome contact increases as endosomes traffic and mature. Friedman, J. R., Dibenedetto, J. R., West, M., Rowland, A. A. & Voeltz, G. K. Mol. Biol. Cell 24, 1030–1040 (2013); permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.