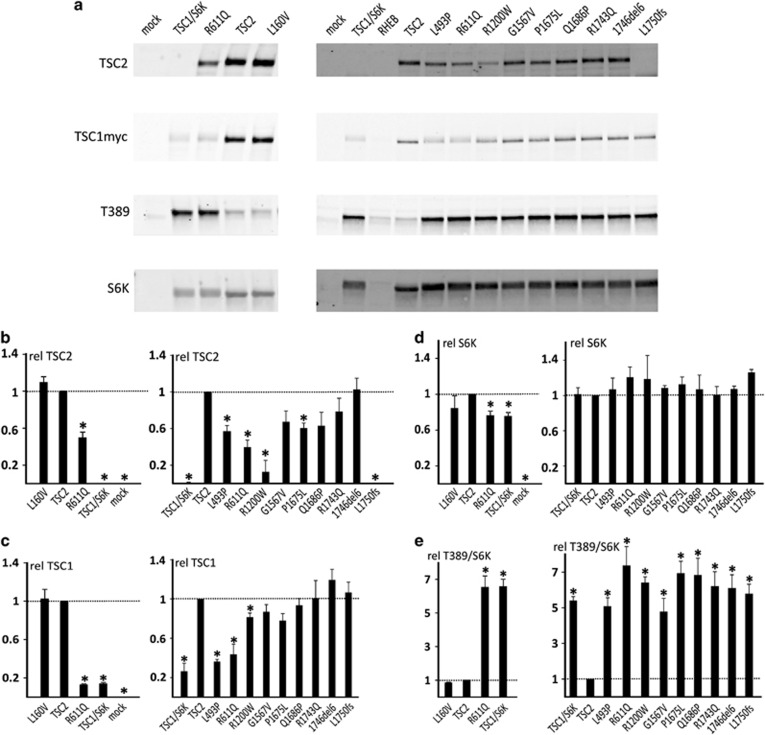
Figure 3.
Functional assessment of TSC2 variants. We compared the effects of expression of wild-type TSC2 with 10 different TSC2 variants in HEK 293T (TSC2−/− 3H9) cells using a transfection-based immunoblot assay. All the variants were identified in our patient cohort with the exception of the p.L1750fs variant. This variant is similar to the TSC2 c.5252_5259+19del27, p.(R1751Hfs*41) variant identified in our cohort. In both cases, the variant mRNA transcript is predicted to escape NMD, and the C-terminal epitope used for TSC2 protein detection is absent. Immunoblots are shown in (a). The signals for TSC2, TSC1, total S6K (S6K) and T389-phosphorylated S6K (T389) were determined per variant, relative to the wild-type control (TSC2) in four transfection experiments. The mean TSC2 (b), TSC1 (c) and S6K (d), signals and mean T389/S6K ratio (e) are shown for each variant. The dotted lines indicate the signal/ratio for TSC2 (=1.0). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean; variants that were significantly different from TSC2 are indicated with an asterisk (P<0.05; Student's t-test). Cells were cotransfected with TSC1 and S6K expression constructs, except for the mock transfected cells (pcDNA3 only). TSC1/S6K refers to cells transfected with the TSC1 and S6K expression constructs only; RHEB refers to cells transfected with an RHEB expression construct. Amino acid changes are given according to the TSC2 reference transcript NM_000548.3. Variants that were significantly different from the wild-type are indicated with an asterisk.