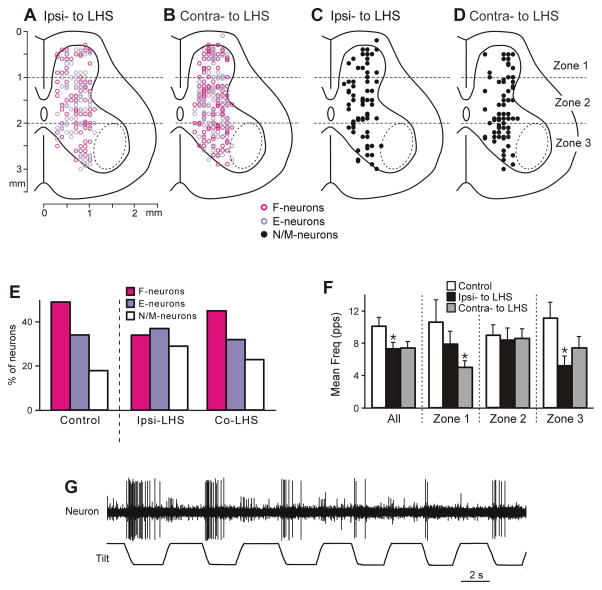
Fig. 4. Neurons recorded during Sur-LHS.
(A,B) Position of all F- and E-neurons on the cross-section of the spinal cord recorded on the side ipsilateral to LHS (A, n=155) and on the side contralateral to LHS (B, n=209). (C,D) Position of all non-modulated neurons on the cross-section of the spinal cord recorded on the side ipsilateral to LHS (C, n=63) and on the side contralateral to LHS (D, n=63). (E) Relative number of F-, E- and non-modulated neurons in control and after LHS (on the side ipsilateral to LHS and on the side contralateral to LHS). (F) Effect of LHS on activity of non-modulated spinal neurons. The mean and SE values of the mean frequency of non-modulated neurons recorded in control and in rabbits with LHS (on the side ipsilateral to the lesion and on the intact side), are shown for the entire population of non-modulated neurons (All), as well as for its sub-populations located in different zones (1–3) of the grey matter. The numbers of non-modulated neurons recorded in zones 1–3 in control were n=14, 27, 23, respectively. The numbers of non-modulated neurons recorded in zones 1–3 in rabbits with LHS on the lesioned and intact side were n=16, 27, 20, and n=13, 26, 24, respectively. (G) Example of a neuron with inconsistent responses to tilt.