Figure 1. Bacterial endophthalmitis reduced AMPK phosphorylation in the retina.
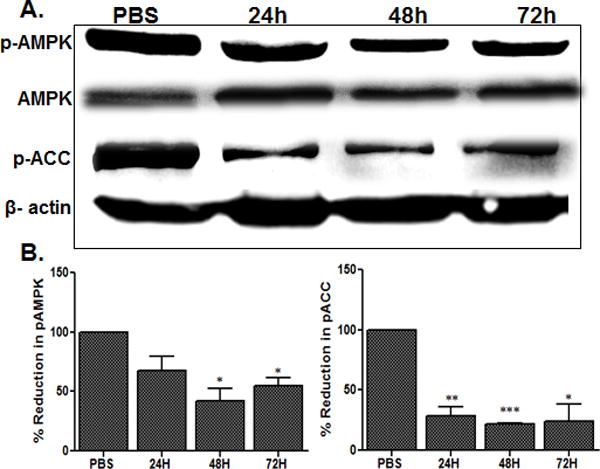
Endophthalmitis was induced by inoculation of S. aureus (RN6390, 5000 cfu) in the eyes of C57BL/6 mice (n = 6/time point). At the indicated time points (except PBS at 24h), the retinas were removed from the infected eyes, pooled (two retinas per sample), and sonicated to make retinal lysates. Following protein quantification, the retinal lysates were used for Western blot detection of total AMPK, phospho(p)-AMPK, and phospho(p)-ACC (A). Antibodies against total AMPK and β-actin were used to normalize protein loading. For quantification, the band intensities were measured using imageJ software and the percentage reduction of p-AMPK and p-ACC in infected samples were calculated with respect to the ratio of p-AMPK/AMPK and p-ACC/β-actin in PBS controls set at 100%, respectively. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments (B). Statistical analysis was performed by using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.001, *** p < 0.0001.
