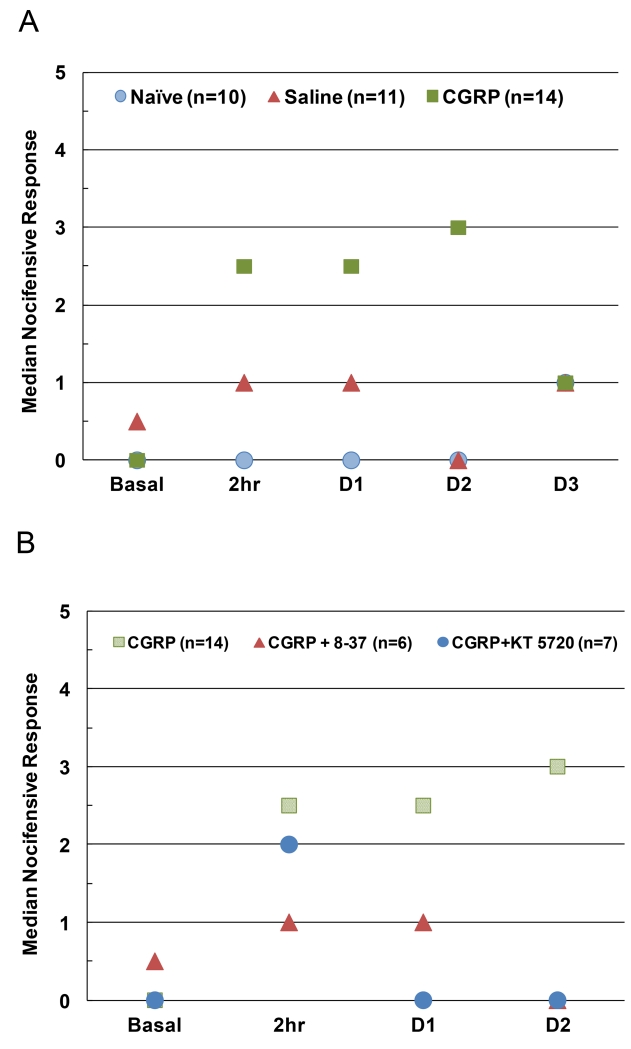
Figure 1.
A. Intracisternal injection of CGRP in upper cervical spinal cord increased nociceptive responses to mechanical stimulation of trigeminal neurons. The median number of nocifensive head withdrawals to the 100 g filament in naïve animals compared to animals basally and at 2 h, 1 day, 2 days, or 3 days post intracisternal injection of saline or CGRP is shown. B. The median number of nocifensive withdrawal responses to the 100 g filament was decreased in a time-dependent manner by inhibiting CGRP or PKA activity. Animals were injected intracisternally with CGRP or co-injected with CGRP and the truncated CGRP receptor antagonist peptide CGRP8-37 (CGRP + 8-37) or the selective PKA inhibitor KT 5720 (CGRP + KT 5720).