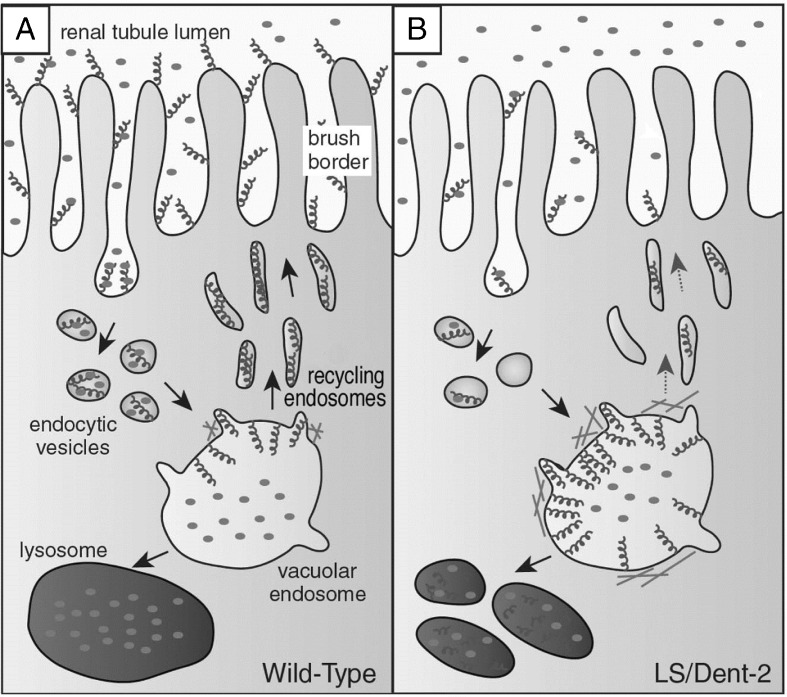
Fig. 1.
Pathogenesis of low-molecular-weight (LMW) proteinuria in Lowe syndrome. LMW proteins (filled circles) are internalized after binding to megalin (helices) on the brush border of proximal tubular cells. a In the wild-type, the megalin–LMW protein complex in the endosome dissociates at low pH, followed by the recycling of megalin to the cell surface and delivery of the LMW proteins to lysosomes for degradation. b In Lowe syndrome/Dent-2 disease, megalin trafficking to the cell surface is impaired. Due to the aberrant accumulation of actin at the endosomal membrane, megalin is retained in the endosome and mis-sorted to the lysosome instead of being recycled to the brush border via recycling tubules (modified from Mehta et al. [33] with permission)