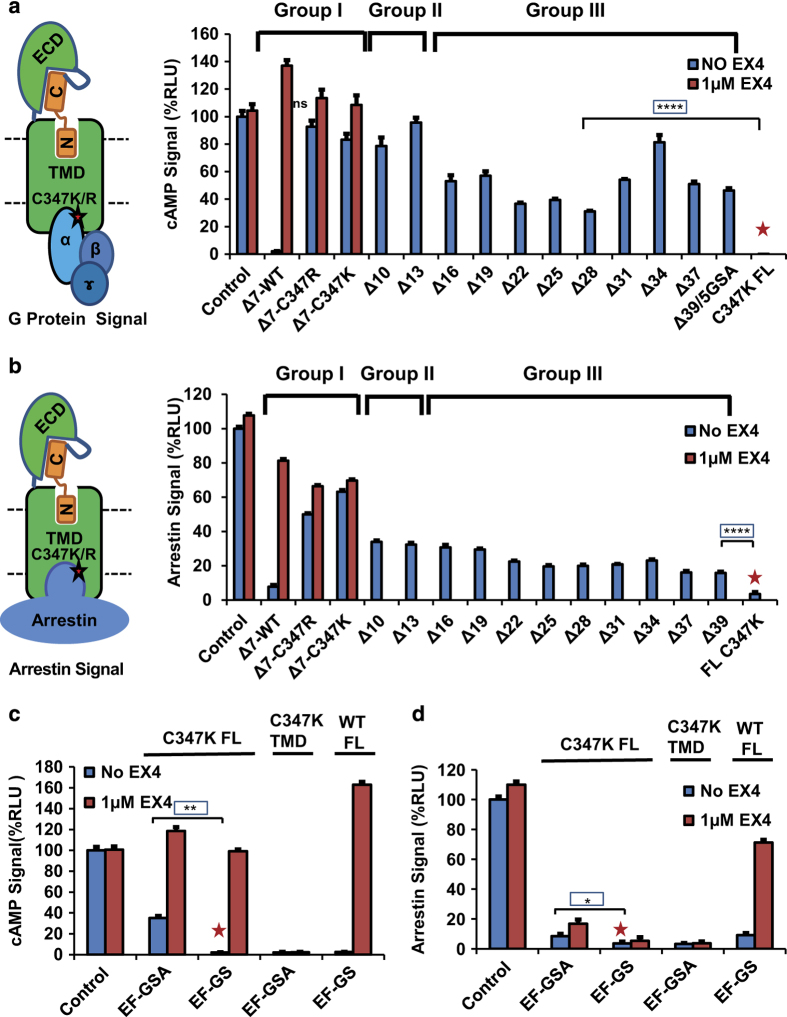
Figure 5.
GLP-1R C347K can be activated by a non-specific five residue linker that is devoid of EX4 or GLP-1 sequence. (a) cAMP signal induced by truncated peptide fused to full-length GLP-1R with C347K mutation. Left, a cartoon presentation of G protein activation by the EX4-5GSA-GLP-1R C347K/R fusion receptor. Group I: EX4(8-39)-5xGSA-GLP-1R WT, and C347K/R mutant. Group II: EX4-5xGSA-GLP-1R C347K with truncations of 10 or 13 N-terminal EX4 residues. Group III: EX4-5xGSA-GLP-1R C347K with truncations of 16–39 (39=all) EX4 residues. (b) Arrestin binding signals induced by sequentially truncated peptide hormone fused to full-length GLP-1R C347K. Left, a cartoon presentation of arrestin recruitment by the same EX4-5xGSA-GLP-1R C347K/R fusion system. Groups I, II and III represent the arrestin binding signals induced by the hormone-GLP-1R mutant systems described in a. (c and d) The cAMP (c) or arrestin binding (d) signals induced by EFGSA linker fused to the N terminus of WT or C347K full-length GLP-1R or GLP-1R TMD. ‘Δ number’ indicates the number of N-terminal residues that were deleted from EX4. Non-fused or EF-GS fused full-length GLP1R C347K was used as negative control (marked by red asterisks). Error bars=s.d., all experiments were performed as three independent transfection experiments. Two-tailed Student’s t test was used to determine P-values, which show no significant difference (NS>0.05) in activation between WT receptor fused with full length EX4 (control) and ∆7-C347K, but there is significant difference in activity between C347K fusion with truncation peptide (group III) and non-fused C347K full-length receptor (marked by red asterisks), which is not active in the absence of exogenous peptide (boxed P-values: *⩽0.05; **⩽0.01; ***⩽0.001; ****⩽0.0001).