Figure 4.
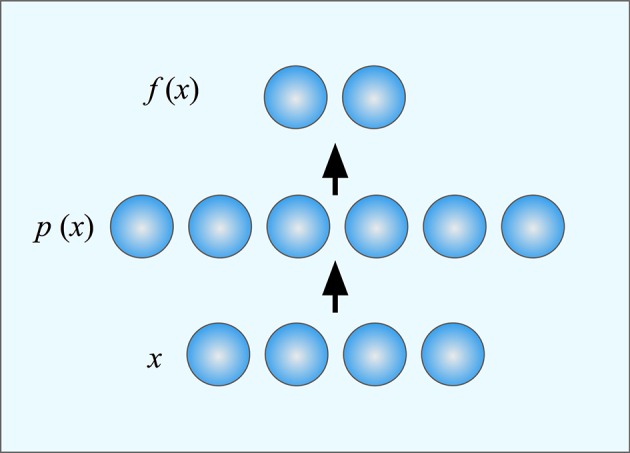
A three-layer neural network. The input x is mapped onto a population code p(x) in a hidden layer where each neuron (or basis unit) is tuned to different position in the input space (its prototype). The output function f(x) is computed by weighting together the responses of the units in the hidden layer. Different functions can be computed by weighting the outputs differently. Learning in the network consists of finding the appropriate weights for the desired function.
