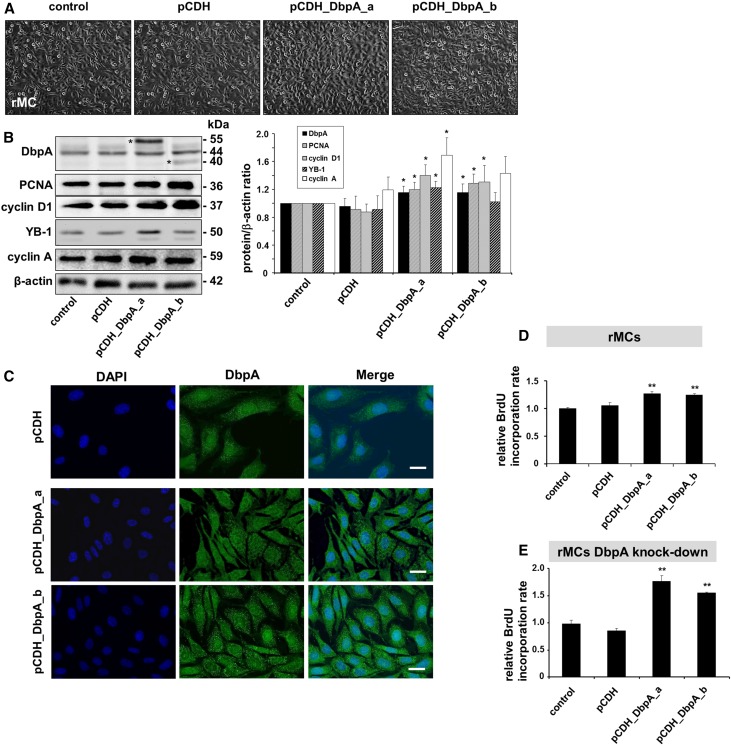
Figure 3.
Overexpression of DbpA in rMCs leads to increased cell proliferation. (A) Cellular morphology of rMCs after overexpression of DbpA isoforms DbpA_a and DbpA_b for 3 days. Both interventions result in increased cells proliferation. (B) Western blot analysis reveals the overexpression of both isoforms of DbpA (40 and 55 kD; asterisks in left panel) by pCDH lentiviral transduction, which is accompanied by upregulation of cell proliferation markers (e.g., PCNA and cyclin D1). *P<0.05 (n=4). (C) Immunofluorescence staining shows both cytoplasmic and nuclear DbpA expression, whereas overexpressed DbpA protein mainly localizes in a punctuate manner within the cytoplasm. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) BrdU cell proliferation assay shows increased cell proliferation in DbpA_a and DbpA_b overexpressing mesangial cells compared with transfection of control vector. **P<0.01 (n=3). (E) Overexpression of DbpA in rMCs with stable knockdown of DbpA leads to much stronger induction of BrdU incorporation. **P<0.01 (n=3).