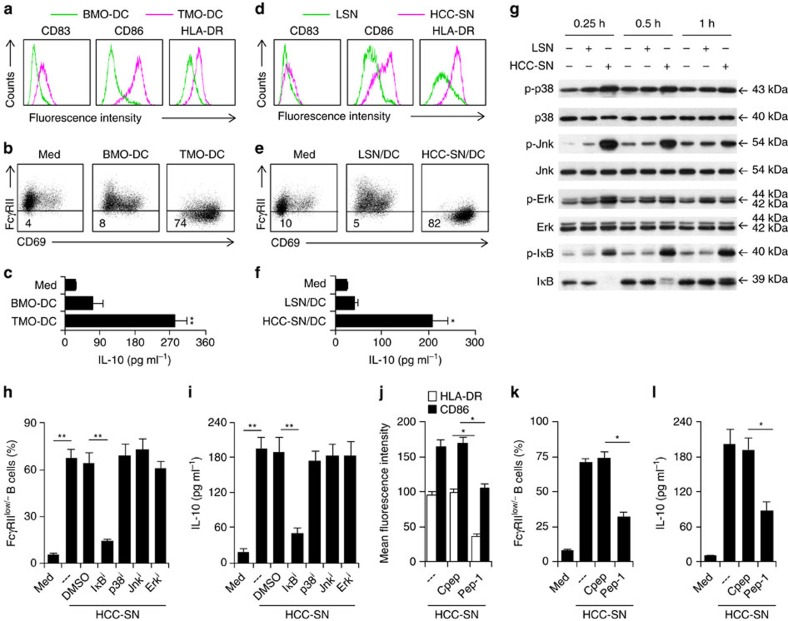
Figure 3. Roles of early activation of monocytes in tumour DC-elicited B-cell activation and subsequent IL-10 production.
(a–f) Peripheral B cells were cultured for 24 h in medium (Med) or with autologous blood or tumour monocyte-derived DCs (BMO-DC or TMO-DC) (a–c); peripheral B cells were cultured for 24 h in medium (Med) or with autologous DCs generated from blood monocytes that were pretreated for 1 h with culture supernatant from primary HCC cells (HCC-SN) or normal liver L02 cells (LSN) (d–f). Thereafter, B cells were purified by CD19+ beads and then culture for additional 24 h in medium alone. Expression of CD83, CD86 and HLA-DR in DCs before co-culture (a,d) and expression of FcγRII in B cells after co-culture (b,e) were determined by FACS. Concentration of IL-10 in culture supernatant was determined by ELISA (c,f). Results represent three independent experiments (n=5). (g) Kinetic effects of HCC-SN and LSN on Erk, p38, Jnk and IκBα activation in monocytes. Results represent three independent experiments (n=4). (h,i) Suppression of IκBα, but not Erk, p38, or Jnk, in HCC-SN-pretreated monocytes attenuated HCC-SN-DC-mediated IL-10-producing FcγRIIlow/− B-cell generation. (j–l) Pre-exposure of monocytes to HCC-SN for 1 h in the presence of a hyaluronan-specific blocking peptide (Pep-1) could partially inhibit the semimaturation of DCs, as well as subsequent generation of IL-10-producing FcγRIIlow/− B cells. Uncropped western blot images are shown in Supplementary Fig. 3c. Results represent three independent experiments (n=4). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (Student's t-test). Error bars, s.e.m.