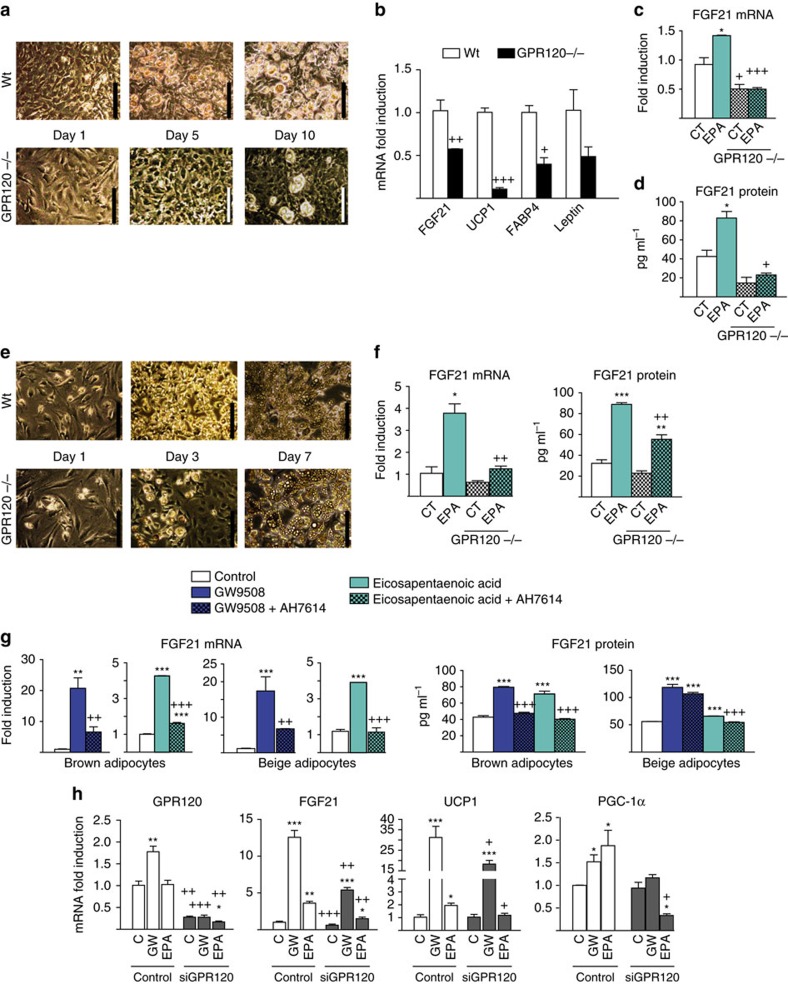
Figure 8. GPR120 is required for the effects of EPA on adipocytes and FGF21 induction and release.
For a–d, iBAT precursors from wild-type (n=3, white) and GPR120-null (n=5, black) mice were differentiated. (a) Representative optical microscopy images (scale bar, 200 μm). (b) Relative mRNA expression levels of FGF21, UCP1, FABP4 and leptin. (c,d) Effects of EPA on FGF21 mRNA expression and FGF21 secretion. For e and f, iWAT precursors from wild-type (n=3) and GPR120-null (n=5) mice were differentiated into beige adipocytes. (e) Representative optical microscopic images (scale bar, 200 μm). (f) Effects of EPA on FGF21 mRNA expression and FGF21 protein secretion. (g) Differentiated brown and beige adipocytes were treated with GW9508 (blue bars) or EPA (turquoise bars) in the presence or absence of AH7614 (a GPR120 antagonist, patterned bars) for 24 h (n=3). FGF21 mRNA expression and FGF21 protein levels in culture medium. (h) Differentiated brown adipocytes were subjected to siRNA-mediated knockdown of GPR120 (see the Methods section) and treated with GW9508 or EPA. mRNA expression levels of GPR120, FGF21, PGC-1α and UCP1 (n=3). Bars are means+s.e.m. (*P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 relative to controls, and +P<0.05, ++P<0.01 and +++P<0.001 for comparisons between wild-type and GPR120-null cells (a–f), the effects due to AH7614 (g), and the effects due to siRNA-GPR120 (h). For b, two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test was performed; for c–h, analysis of variance with Tukey's post hoc test).