Figure 3.
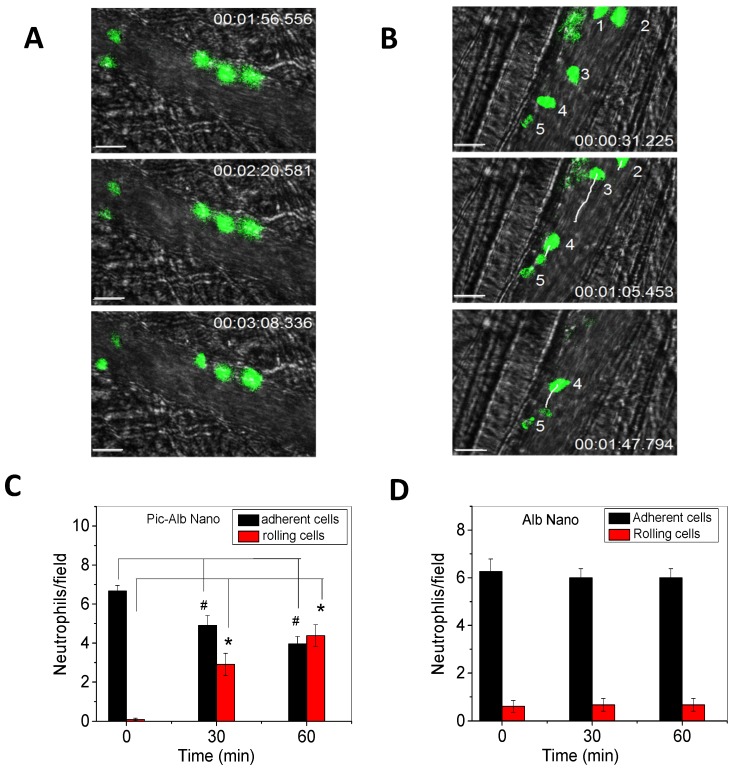
Therapeutic effects of drug-loaded albumin nanoparticles are evaluated using IVM. IVM of cremaster venules showing adhesion and rolling of neutrophils (green) labeled by Alexa Fluor-488 anti-mouse Gr-1 antibody in a mouse before (a) and at 1 h after intravenous injection of piceatannol-loaded albumin nanoparticles (b) in the same mouse. hh:mm:ss represents time series of images. The white lines show the trajectories of neutrophils detaching from endothelium. Scale bar, 20 µm. (c) Quantification of neutrophil adhesion and rolling in TNF-α-activated cremaster venules at the baseline, and at 30 and 60 min after intravenous infusion of piceatannol-loaded albumin nanoparticles. Data represent mean±s.e.m (n=21 venules in three mice). *p<0.01 and *p<0.001 versus pre-infusion of nanoparticles. (d) albumin nanoparticles without piceatannol were tested and quantified as described in c. Data represent mean±s.e.m. (n=18 venules in three mice). The images are reproduced and permitted from the reference 24.