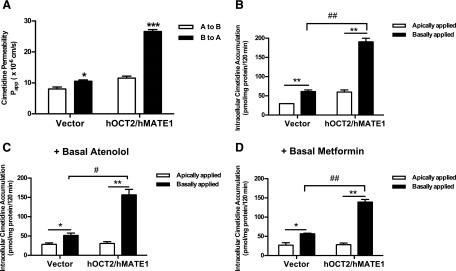
Fig. 5.
Cimetidine permeability and intracellular accumulation in MDCK-hOCT2/hMATE1 cells. Vector- and hOCT2/hMATE1-transfected MDCK cells growing on inserts were incubated in KRH buffer with [3H]cimetidine (10 μM) added to either apical (pH 6.0) or basal chamber (pH 7.4). An aliquot of buffer in the receiving chamber was sampled periodically up to 120 minutes. (A) Cimetidine permeability in the B-to-A and A-to-B directions was measured and compared (***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05). (B–D) Intracellular accumulation of [3H]cimetidine (10 μM) after application to basal or apical chamber alone or with cold atenolol (1 μM) or metformin (5.5 μM) added in the basal chamber. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 indicates significantly higher accumulation when cimetidine was applied to the basal chamber compared with the apical chamber. ##P < 0.01, #P < 0.05 indicate significantly higher accumulation in hOCT2/hMATE1 cells compared with vector control. Experiments were performed in two to three individual Transwell apparatuses and repeated twice. Data were presented as mean ±S.D. (n = 6) of all apparatuses with acceptable TEER values.