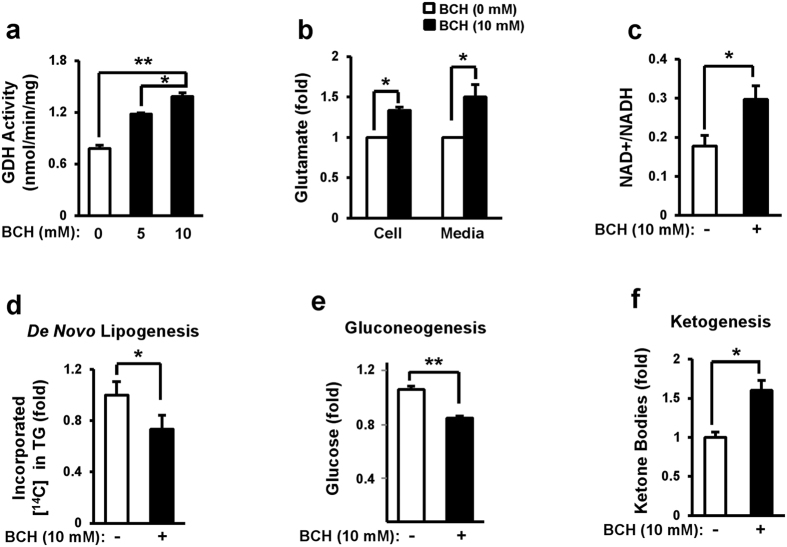
Figure 1. Stimulation of reductive amination through treatment with glutamate dehydrogenase activator BCH reduced de novo lipogenesis and gluconeogenesis while enhanced ketogenesis in primary hepatocytes.
(a) GDH activity, (b) glutamate level, and (c) NAD+/NADH ratio were measured in primary hepatocytes treated with BCH for 12 h using respective assay kits. (d) De novo lipogenesis was determined by measuring incorporation of D-[U-14C]-glucose into triacyglycerol (TG). (e) Glucose production from lactate and pyruvate was determined by measuring the amount of glucose released from hepatocytes. (f) Ketogenesis was determined by measuring the amount of the released ketone bodies. Data were represented as means ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. BCH-untreated group.