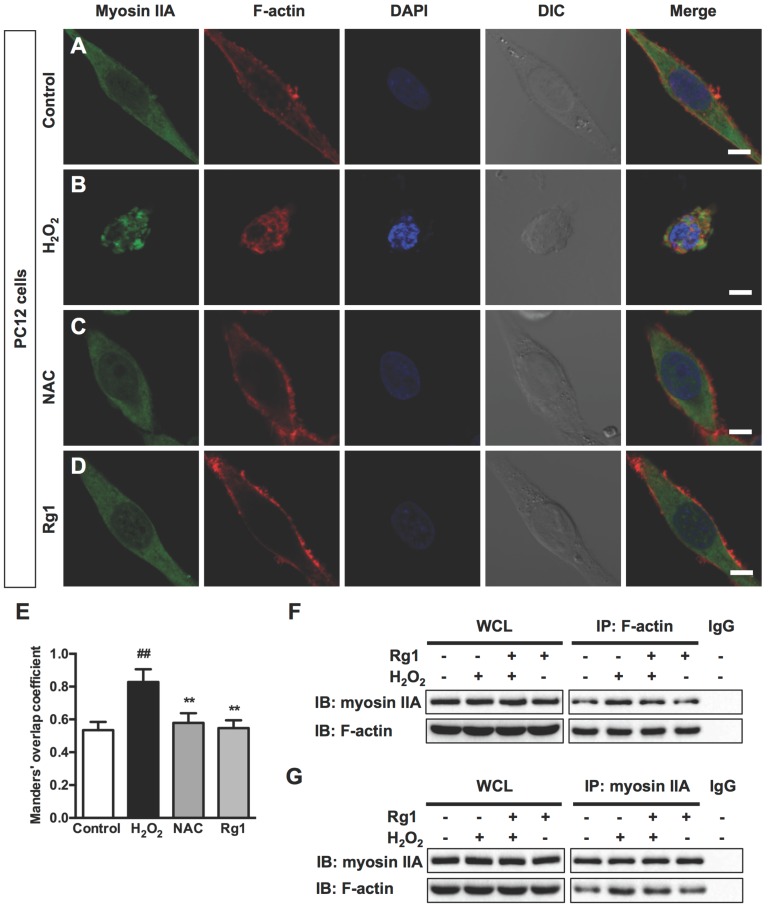
Figure 5.
Rg1 attenuates H2O2-induced myosin IIA-actin interaction in PC12 cells. PC12 cells were pre-treated with 10 μM Rg1 for 12 h prior to 100 μM H2O2 treatment for 12 h. Positive control was treated with NAC (500 µM). (A-D) Immunofluorescence of myosin IIA and F-actin under confocal microscopy. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Differential interference contrast (DIC) images were also obtained. Bar, 10 μM. (E) The quantitative colocalization of myosin IIA with F-actin was evaluated on basis of Manders' overlap coefficients. Results were expressed as mean ± SD from three independent experiments (##P< 0.01 versus control, **P< 0.01 versus H2O2-treated cells). Co-immunoprecipitation of myosin IIA and actin was detected by Western blots with indicated antibodies. The bands of left panel are from whole cell lysates (WCL) and the bands of right panel are the same as shown on the left but immunoprecipitated with indicated antibodies. After treatment, cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-F-actin antibody (F) or anti-myosin IIA antibody (G), and then the precipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-myosin IIA and anti-F-actin antibodies. Whole cell lysates (WCL) and immunoprecipitates with normal IgG were loaded as positive and negative controls, respectively. IB: immunoblotting, IP: immunoprecipitation and IgG: immunoglobulin G.