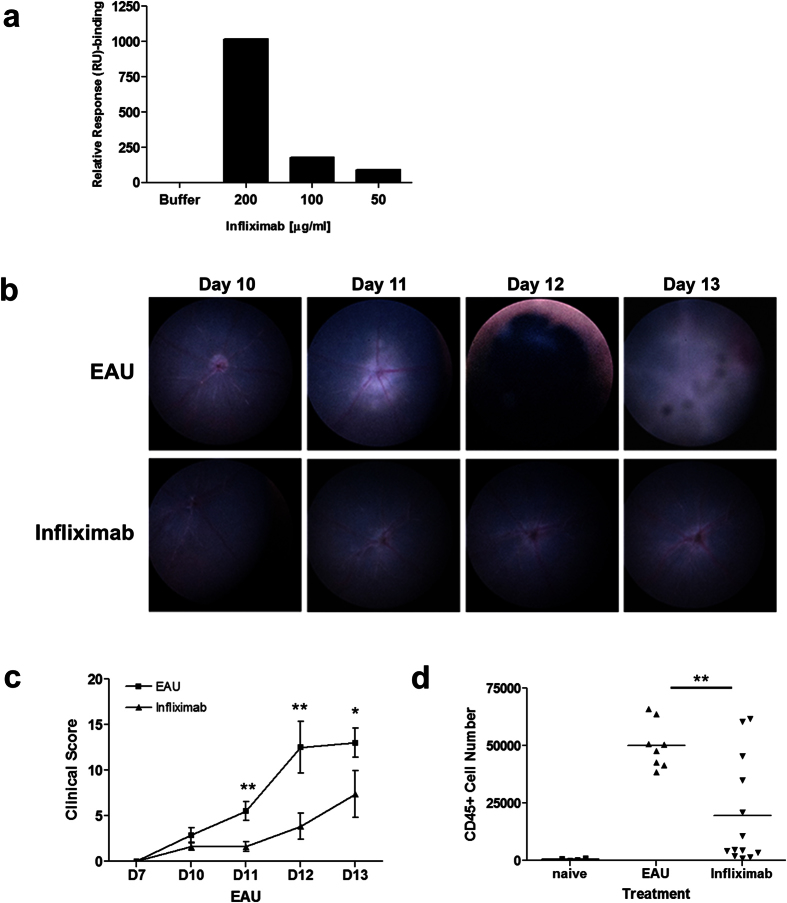
Figure 1. Local administration of infliximab suppresses EAU.
(a) Graph detailing the Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) binding analysis, confirming that infliximab can bind to murine TNF-α using a NTA chip. (b–d) Mice were immunized for EAU and eyes monitored using TEFI from day 10 onward to select experimental mice displaying clinically evident disease. Groups of mice were injected via intravitreal route with 15 μg infliximab or vehicle control (EAU) on day 10. Eyes were enucleated on day 14, and retinal infiltrate characterized and quantified; (b) Representative TEFI images and (c) combined total disease scores demonstrating the difference in clinical disease progression between treatment groups. In EAU control eyes typical disease progression with signs of raised optic disc, vasculitis and severe inflammation; In infliximab treated eyes, only raised optic disc and initial signs of vasculitis are evident. (d) Graph showing total CD45+ infiltrate numbers from individual eyes. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005; Data presented as means ± SEM, and representative of two independent experiments.