Fig. 2.
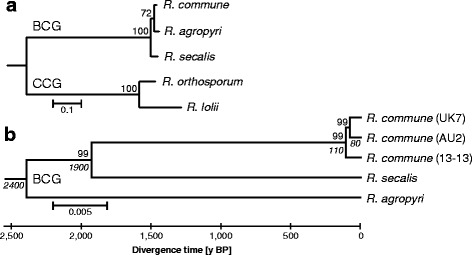
Rhynchosporium evolutionary relationships. a Rhynchosporium subtree of the Leotiomycetes phylogeny (cf. Additional file 1: Figure S1). The nucleotide sequences of 18S rDNA, 28S rDNA, ITS region, elongation factor EF1-a and RNA polymerase II subunits RPB1 and RPB2 were concatenated. b SNP-based phylogeny of the BCG species including the three R. commune isolates UK7, AU2 and 13-13. The evolutionary history was inferred using the Minimum Evolution method (optimal tree with sum of branch length = 1.022). The tree is drawn to scale. All nucleotide positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated, leaving a final dataset of 5,904,161 positions. Scale: number of substitutions per site and SNPs per position, respectively. Bootstrap numbers are given above branching points, divergence times in italics below branching points. BCG, beaked conidia group; CCG, cylindrical conidia group
