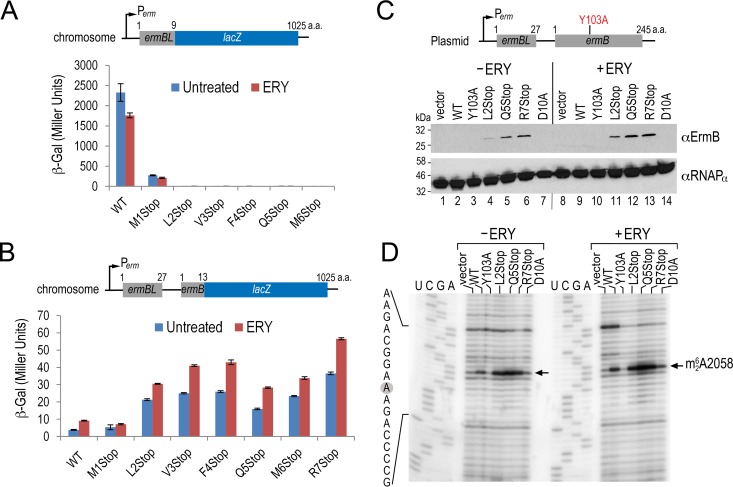
FIG 2.
ErmBLEF nonsense mutations result in a high basal and inducible expression of downstream ErmB that is consistent with the cellular concentrations of ErmB and the degree of ribosome methylation. (A) A β-galactosidase activity assay showing that nonsense mutations at residues L2 through R7 effectively shut down lacZ synthesis and revealing that L2 acts as an alternate start codon. β-Galactosidase activity (in Miller units) was conducted with E. coli bearing the chromosomal ermBL′-lacZ with or without 30 min of erythromycin (ERY) exposure. ERY was used at 100 μg/ml. (B) Results from a β-galactosidase assay showing that none of the premature nonsense mutations after codon M1 abolishes the downstream ermB′-lacZ expression. The β-galactosidase activity was determined as described in panel A except that chromosomal ermBL-ermB′-lacZ fusion was used. Error bars indicate standard deviations from three replicates. (C) Western blot analysis shows that ErmB overexpression remains inducible in response to ERY and that the degree of induction correlates with the lacZ reporter results. Log-phase cells with or without 30 min of ERY treatment were harvested and sonicated, and 40-μg portions of total soluble proteins were loaded per lane on the SDS-PAGE gel. Y103A is a catalytically inactive ErmB mutant. The alpha-subunit of RNA polymerase served as the loading control. A 1/1,000 dilution of anti-ErmB and a 1 1/10,000 dilution of anti-RNAPα were used for immunoblotting. (D) Results from a primer extension assay showing that the magnitude of A2058 methylation is consistent with the cellular levels of ErmB. Total RNAs were isolated from the same cells shown in panel C and used at 250 ng per lane. In primer extension, the reverse transcriptase halts at the methylated site and produces a truncated cDNA that is manifested by a strong signal at A2058.