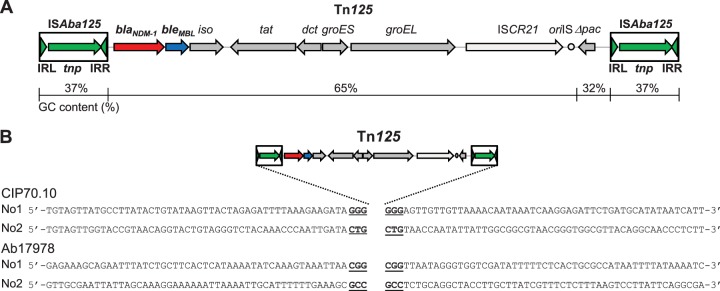
FIG 1.
Transposition of Tn125. (A) Schematic representation of transposon Tn125. The total size is 10,099 bp. The ORFs are represented by arrows, and the lengths are to scale. The two ISAba125 elements bracketing Tn125 are indicated in green, each with the transposase (tnp) gene and the IRL and IRR inverted repeats. The blaNDM-1 gene is in red, the bleMBL gene is in blue, and the 7 other ORFs are in dark gray; the ISCR21 and the oriIS (circle) are in light gray. The GC content (%) for each of the following fragments is indicated: 37% for each ISAba125 (nucleotides 1 to 1087 and 9013 to 10099), 65% for the sequence encompassing blaNDM-1 to oriIS, and 32% for Δpac. (B) Characterization of four Tn125 transposition events in A. baumannii CIP70.10 and Ab17978 (recA mutant) strains. The duplicated 3-bp target sites are underlined. The surrounding 50 nucleotides, upstream and downstream of each transposon insertion, are shown. In A. baumannii CIP70.10, transposon Tn125 transposed between ORFs designated No1 (encoding proteins deposited under accession no. CRL92855.1 and CRL92856.1) or an ORF designated No2 (encoding an outer membrane protein A precursor [accession no. CRL95910.1); in A. baumannii Ab17978 (recA mutant), transposon Tn125 transposed in the ORF designated No1 (encoding a hypothetical protein [accession no. AKQ26110.1]) or in the ORF designated No2 (encoding a CinA-like protein [accession no. KNZ37258.1]).